Custom Routing for LLM Prompts with Not Diamond
This notebook demonstrates how to use Weave with Not Diamond's custom routing to route LLM prompts to the most appropriate model based on evaluation results.
Routing prompts
When building complex LLM workflows users may need to prompt different models according to accuracy, cost, or call latency. Users can use Not Diamond to route prompts in these workflows to the right model for their needs, helping maximize accuracy while saving on model costs.
For any given distribution of data, rarely will one single model outperform every other model on every single query. By combining together multiple models into a "meta-model" that learns when to call each LLM, you can beat every individual model's performance and even drive down costs and latency in the process.
Custom routing
You need three things to train a custom router for your prompts:
- A set of LLM prompts: Prompts must be strings and should be representative of the prompts used in our application.
- LLM responses: The responses from candidate LLMs for each input. Candidate LLMs can include both our supported LLMs and your own custom models.
- Evaluation scores for responses to the inputs from candidate LLMs: Scores are numbers, and can be any metric that fit your needs.
By submitting these to the Not Diamond API you can then train a custom router tuned to each of your workflows.
Setting up the training data
In practice, you will use your own Evaluations to train a custom router. For this example notebook, however, you will use LLM responses for the HumanEval dataset to train a custom router for coding tasks.
We start by downloading the dataset we have prepared for this example, then parsing LLM responses into EvaluationResults for each model.
!curl -L "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1q1zNZHioy9B7M-WRjsJPkfvFosfaHX38" -o humaneval.csv
import random
import weave
from weave.flow.dataset import Dataset
from weave.flow.eval import EvaluationResults
from weave.integrations.notdiamond.util import get_model_evals
pct_train = 0.8
pct_test = 1 - pct_train
# In practice, you will build an Evaluation on your dataset and call
# `evaluation.get_eval_results(model)`
model_evals = get_model_evals("./humaneval.csv")
model_train = {}
model_test = {}
for model, evaluation_results in model_evals.items():
n_results = len(evaluation_results.rows)
all_idxs = list(range(n_results))
train_idxs = random.sample(all_idxs, k=int(n_results * pct_train))
test_idxs = [idx for idx in all_idxs if idx not in train_idxs]
model_train[model] = EvaluationResults(
rows=weave.Table([evaluation_results.rows[idx] for idx in train_idxs])
)
model_test[model] = Dataset(
rows=weave.Table([evaluation_results.rows[idx] for idx in test_idxs])
)
print(
f"Found {len(train_idxs)} train rows and {len(test_idxs)} test rows for {model}."
)
Training a custom router
Now that you have EvaluationResults, you can train a custom router. Make sure you have created an account and generated an API key, then insert your API key below.
import os
from weave.integrations.notdiamond.custom_router import train_router
api_key = os.getenv("NOTDIAMOND_API_KEY", "<YOUR_API_KEY>")
preference_id = train_router(
model_evals=model_train,
prompt_column="prompt",
response_column="actual",
language="en",
maximize=True,
api_key=api_key,
# Leave this commented out to train your first custom router
# Uncomment this to retrain your custom router in place
# preference_id=preference_id,
)
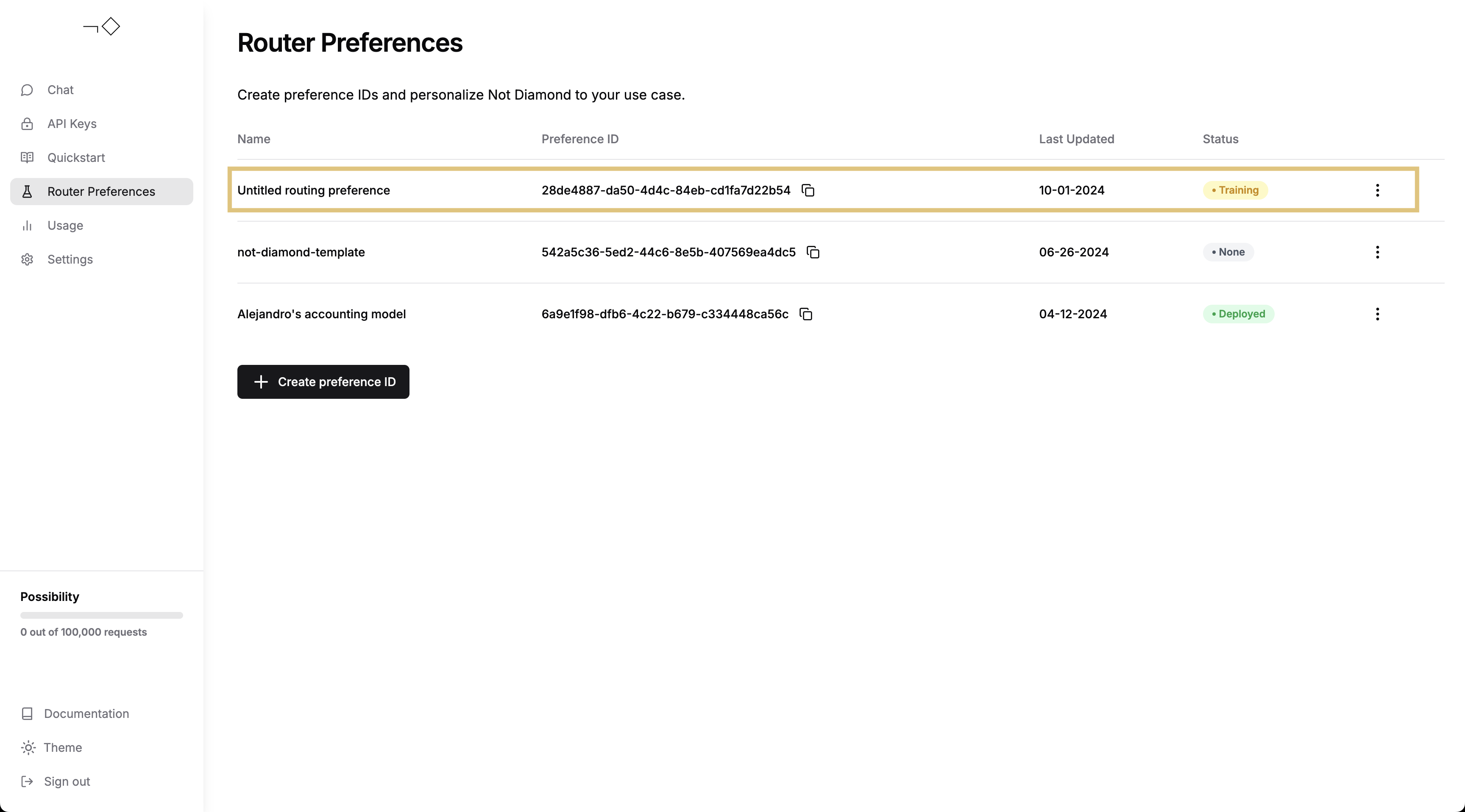
You can then follow the training process for your custom router via the Not Diamond app.
Once your custom router has finished training, you can use it to route your prompts.
from notdiamond import NotDiamond
import weave
weave.init("notdiamond-quickstart")
llm_configs = [
"anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620",
"openai/gpt-4o-2024-05-13",
"google/gemini-1.5-pro-latest",
"openai/gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09",
"anthropic/claude-3-opus-20240229",
]
client = NotDiamond(api_key=api_key, llm_configs=llm_configs)
new_prompt = (
"""
You are a helpful coding assistant. Using the provided function signature, write the implementation for the function
in Python. Write only the function. Do not include any other text.
from typing import List
def has_close_elements(numbers: List[float], threshold: float) -> bool:
"""
""" Check if in given list of numbers, are any two numbers closer to each other than
given threshold.
>>> has_close_elements([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], 0.5)
False
>>> has_close_elements([1.0, 2.8, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 2.0], 0.3)
True
"""
"""
"""
)
session_id, routing_target_model = client.model_select(
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": new_prompt}],
preference_id=preference_id,
)
print(f"Session ID: {session_id}")
print(f"Target Model: {routing_target_model}")
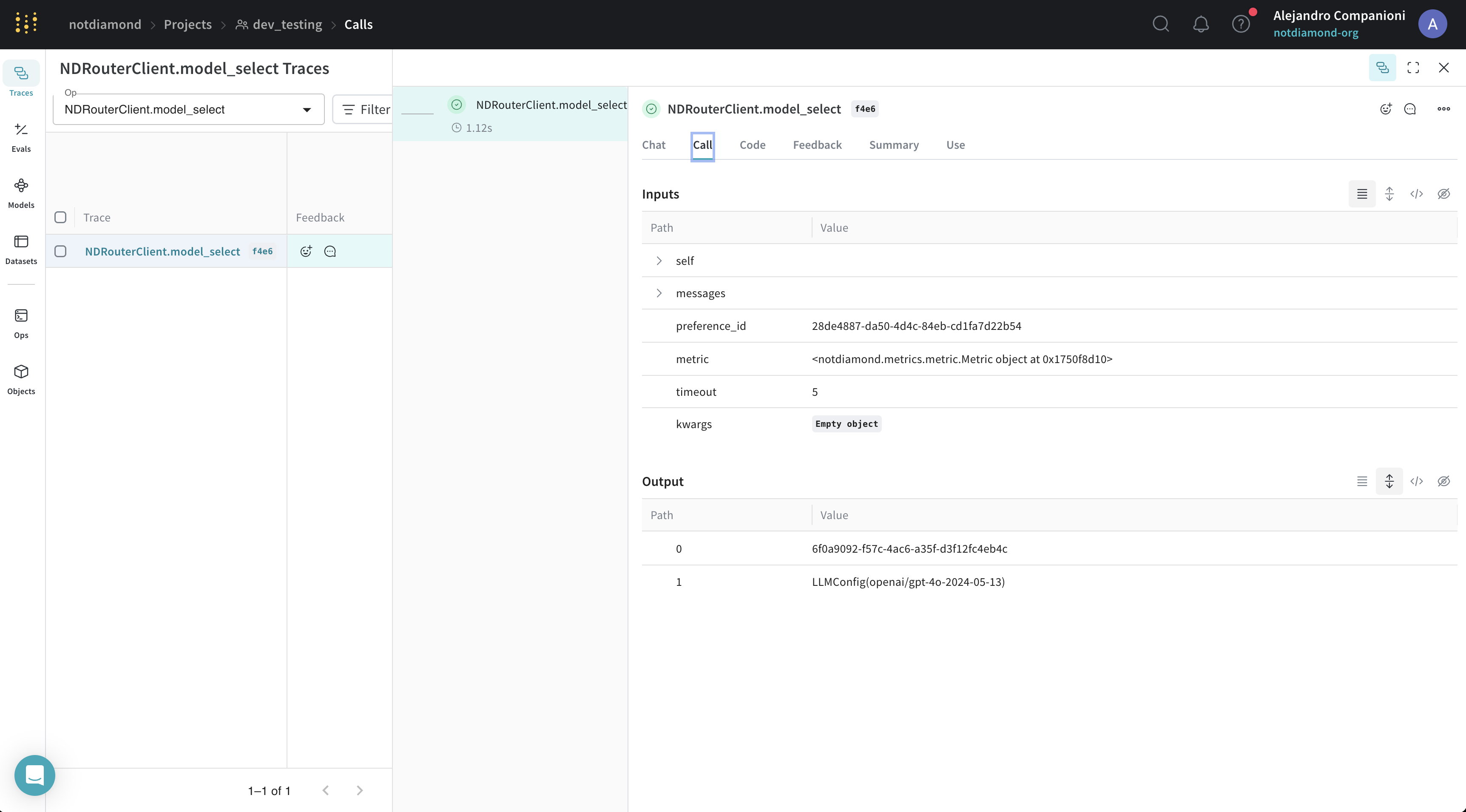
This example also used Not Diamond's compatibility with Weave auto-tracing. You can see the results in the Weave UI.
Evaluating your custom router
Once you have trained your custom router, you can evaluate either its
- in-sample performance by submitting the training prompts, or
- out-of-sample performance by submitting new or held-out prompts
Below, we submit the test set to the custom router to evaluate its performance.
from weave.integrations.notdiamond.custom_router import evaluate_router
eval_prompt_column = "prompt"
eval_response_column = "actual"
best_provider_model, nd_model = evaluate_router(
model_datasets=model_test,
prompt_column=eval_prompt_column,
response_column=eval_response_column,
api_key=api_key,
preference_id=preference_id,
)
@weave.op()
def is_correct(score: int, output: dict) -> dict:
# We hack score, since we already have model responses
return {"correct": score}
best_provider_eval = weave.Evaluation(
dataset=best_provider_model.model_results.to_dict(orient="records"),
scorers=[is_correct],
)
await best_provider_eval.evaluate(best_provider_model)
nd_eval = weave.Evaluation(
dataset=nd_model.model_results.to_dict(orient="records"), scorers=[is_correct]
)
await nd_eval.evaluate(nd_model)
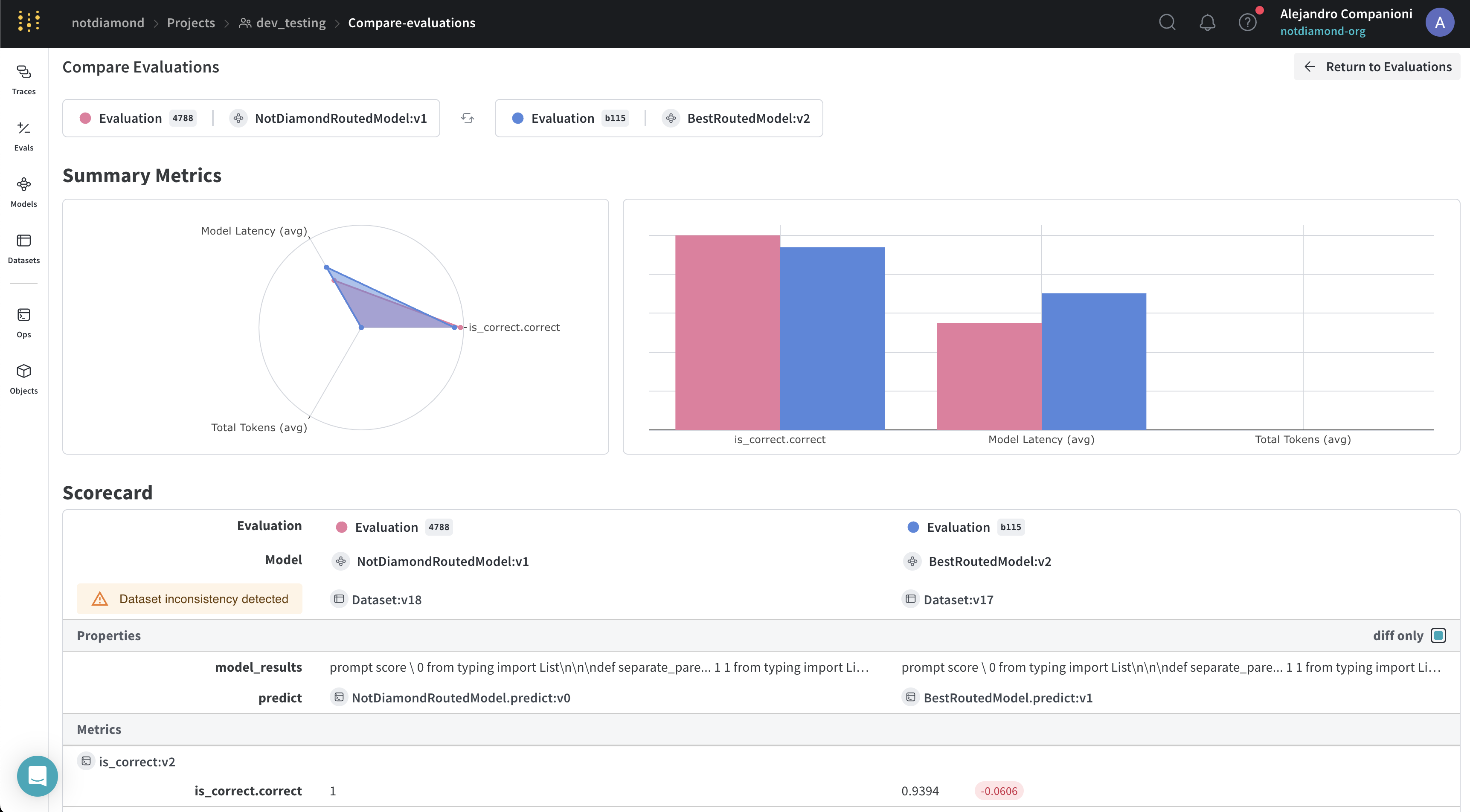
In this instance, the Not Diamond "meta-model" routes prompts across several different models.
Training the custom router via Weave will also run evaluations and upload results to the Weave UI. Once the custom router process is completed, you can review the results in the Weave UI.
In the UI we see that the Not Diamond "meta-model" outperforms the best-performing model by routing prompts to other models with higher likelihood of answering the prompt accurately.