How to use Weave with PII data
In this guide, you'll learn how to use W&B Weave while ensuring your Personally Identifiable Information (PII) data remains private. The guide demonstrates the following methods to identify, redact and anonymize PII data:
- Regular expressions to identify PII data and redact it.
- Microsoft's Presidio, a python-based data protection SDK. This tool provides redaction and replacement functionalities.
- Faker, a Python library to generate fake data, combined with Presidio to anonymize PII data.
Additionally, you'll learn how to use weave.op input/output logging customization and autopatch_settings to integrate PII redaction and anonymization into the workflow. For more information, see Customize logged inputs and outputs.
To get started, do the following:
- Review the Overview section.
- Complete the prerequisites.
- Review the available methods for identifying, redacting and anonymizing PII data.
- Apply the methods to Weave calls.
Overview
The following section provides an overview of input and output logging using weave.op, as well as best practices for working with PII data in Weave.
Customize input and output logging using weave.op
Weave Ops allow you to define input and output postprocessing functions. Using these functions, you can modify the data that is passed to your LLM call or logged to Weave.
In the following example, two postprocessing functions are defined and passed as arguments to weave.op().
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Any
import weave
# Inputs Wrapper Class
@dataclass
class CustomObject:
x: int
secret_password: str
# First we define functions for input and output postprocessing:
def postprocess_inputs(inputs: dict[str, Any]) -> dict[str, Any]:
return {k:v for k,v in inputs.items() if k != "hide_me"}
def postprocess_output(output: CustomObject) -> CustomObject:
return CustomObject(x=output.x, secret_password="REDACTED")
# Then, when we use the `@weave.op` decorator, we pass these processing functions as arguments to the decorator:
@weave.op(
postprocess_inputs=postprocess_inputs,
postprocess_output=postprocess_output,
)
def some_llm_call(a: int, hide_me: str) -> CustomObject:
return CustomObject(x=a, secret_password=hide_me)
Best practices for using Weave with PII data
Before using Weave with PII data, review the best practices for using Weave with PII data.
During testing
- Log anonymized data to check PII detection
- Track PII handling processes with Weave Traces
- Measure anonymization performance without exposing real PII
In production
- Never log raw PII
- Encrypt sensitive fields before logging
Encryption tips
- Use reversible encryption for data you need to decrypt later
- Apply one-way hashing for unique IDs you don't need to reverse
- Consider specialized encryption for data you need to analyze while encrypted
Prerequisites
- First, install the required packages.
%%capture
# @title required python packages:
!pip install cryptography
!pip install presidio_analyzer
!pip install presidio_anonymizer
!python -m spacy download en_core_web_lg # Presidio uses spacy NLP engine
!pip install Faker # we'll use Faker to replace PII data with fake data
!pip install weave # To leverage Traces
!pip install set-env-colab-kaggle-dotenv -q # for env var
!pip install anthropic # to use sonnet
!pip install cryptography # to encrypt our data
%%capture
# @title Make sure to set up set up your API keys correctly
# See: https://pypi.org/project/set-env-colab-kaggle-dotenv/ for usage instructions.
from set_env import set_env
_ = set_env("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY")
_ = set_env("WANDB_API_KEY")
- Initialize your Weave project.
import weave
# Start a new Weave project
WEAVE_PROJECT = "pii_cookbook"
weave.init(WEAVE_PROJECT)
- Load the demo PII dataset, which contains 10 text blocks.
import requests
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wandb/weave/master/docs/notebooks/10_pii_data.json"
response = requests.get(url)
pii_data = response.json()
print('PII data first sample: "' + pii_data[0]["text"] + '"')
Redaction methods overview
Once you've completed the prerequisites, you can
To detect and protect our PII data, we'll identify and redact PII data and optionally anonymize it using the following methods:
- Regular expressions to identify PII data and redact it.
- Microsoft Presidio, a Python-based data protection SDK that provides redaction and replacement functionality.
- Faker, a Python library for generating fake data.
Method 1: Filter using regular expressions
Regular expressions (regex) are the simplest method to identify and redact PII data. Regex allows you to define patterns that can match various formats of sensitive information like phone numbers, email addresses, and social security numbers. Using regex, you can scan through large volumes of text and replace or redact information without the need for more complex NLP techniques.
import re
# Define a function to clean PII data using regex
def redact_with_regex(text):
# Phone number pattern
# \b : Word boundary
# \d{3} : Exactly 3 digits
# [-.]? : Optional hyphen or dot
# \d{3} : Another 3 digits
# [-.]? : Optional hyphen or dot
# \d{4} : Exactly 4 digits
# \b : Word boundary
text = re.sub(r"\b\d{3}[-.]?\d{3}[-.]?\d{4}\b", "<PHONE>", text)
# Email pattern
# \b : Word boundary
# [A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+ : One or more characters that can be in an email username
# @ : Literal @ symbol
# [A-Za-z0-9.-]+ : One or more characters that can be in a domain name
# \. : Literal dot
# [A-Z|a-z]{2,} : Two or more uppercase or lowercase letters (TLD)
# \b : Word boundary
text = re.sub(
r"\b[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,}\b", "<EMAIL>", text
)
# SSN pattern
# \b : Word boundary
# \d{3} : Exactly 3 digits
# - : Literal hyphen
# \d{2} : Exactly 2 digits
# - : Literal hyphen
# \d{4} : Exactly 4 digits
# \b : Word boundary
text = re.sub(r"\b\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}\b", "<SSN>", text)
# Simple name pattern (this is not comprehensive)
# \b : Word boundary
# [A-Z] : One uppercase letter
# [a-z]+ : One or more lowercase letters
# \s : One whitespace character
# [A-Z] : One uppercase letter
# [a-z]+ : One or more lowercase letters
# \b : Word boundary
text = re.sub(r"\b[A-Z][a-z]+ [A-Z][a-z]+\b", "<NAME>", text)
return text
Let's test the function with a sample text:
# Test the function
test_text = "My name is John Doe, my email is john.doe@example.com, my phone is 123-456-7890, and my SSN is 123-45-6789."
cleaned_text = redact_with_regex(test_text)
print(f"Raw text:\n\t{test_text}")
print(f"Redacted text:\n\t{cleaned_text}")
Method 2: Redact using Microsoft Presidio
The next method involves complete removal of PII data using Microsoft Presidio. Presidio redacts PII and replaces it with a placeholder representing the PII type. For example, Presidio replaces Alex in "My name is Alex" with <PERSON>.
Presidio comes with a built-in support for common entities. In the below example, we redact all entities that are a PHONE_NUMBER, PERSON, LOCATION, EMAIL_ADDRESS or US_SSN. The Presidio process is encapsulated in a function.
from presidio_analyzer import AnalyzerEngine
from presidio_anonymizer import AnonymizerEngine
# Set up the Analyzer, which loads an NLP module (spaCy model by default) and other PII recognizers.
analyzer = AnalyzerEngine()
# Set up the Anonymizer, which will use the analyzer results to anonymize the text.
anonymizer = AnonymizerEngine()
# Encapsulate the Presidio redaction process into a function
def redact_with_presidio(text):
# Analyze the text to identify PII data
results = analyzer.analyze(
text=text,
entities=["PHONE_NUMBER", "PERSON", "LOCATION", "EMAIL_ADDRESS", "US_SSN"],
language="en",
)
# Anonymize the identified PII data
anonymized_text = anonymizer.anonymize(text=text, analyzer_results=results)
return anonymized_text.text
Let's test the function with a sample text:
text = "My phone number is 212-555-5555 and my name is alex"
# Test the function
anonymized_text = redact_with_presidio(text)
print(f"Raw text:\n\t{text}")
print(f"Redacted text:\n\t{anonymized_text}")
Method 3: Anonymize with replacement using Faker and Presidio
Instead of redacting text, you can anonymize it by using MS Presidio to swap PII like names and phone numbers with fake data generated using the Faker Python library. For example, suppose you have the following data:
"My name is Raphael and I like to fish. My phone number is 212-555-5555"
Once the data has been processed using Presidio and Faker, it might look like:
"My name is Katherine Dixon and I like to fish. My phone number is 667.431.7379"
To effectively use Presidio and Faker together, we must supply references to our custom operators. These operators will direct Presidio to the Faker functions responsible for swapping PII with fake data.
from faker import Faker
from presidio_anonymizer import AnonymizerEngine
from presidio_anonymizer.entities import OperatorConfig
fake = Faker()
# Create faker functions (note that it has to receive a value)
def fake_name(x):
return fake.name()
def fake_number(x):
return fake.phone_number()
# Create custom operator for the PERSON and PHONE_NUMBER" entities
operators = {
"PERSON": OperatorConfig("custom", {"lambda": fake_name}),
"PHONE_NUMBER": OperatorConfig("custom", {"lambda": fake_number}),
}
text_to_anonymize = (
"My name is Raphael and I like to fish. My phone number is 212-555-5555"
)
# Analyzer output
analyzer_results = analyzer.analyze(
text=text_to_anonymize, entities=["PHONE_NUMBER", "PERSON"], language="en"
)
anonymizer = AnonymizerEngine()
# do not forget to pass the operators from above to the anonymizer
anonymized_results = anonymizer.anonymize(
text=text_to_anonymize, analyzer_results=analyzer_results, operators=operators
)
print(f"Raw text:\n\t{text_to_anonymize}")
print(f"Anonymized text:\n\t{anonymized_results.text}")
Let's consolidate our code into a single class and expand the list of entities to include the additional ones identified earlier.
from typing import ClassVar
from faker import Faker
from presidio_anonymizer import AnonymizerEngine
from presidio_anonymizer.entities import OperatorConfig
# A custom class for generating fake data that extends Faker
class MyFaker(Faker):
# Create faker functions (note that it has to receive a value)
def fake_address(self):
return fake.address()
def fake_ssn(self):
return fake.ssn()
def fake_name(self):
return fake.name()
def fake_number(self):
return fake.phone_number()
def fake_email(self):
return fake.email()
# Create custom operators for the entities
operators: ClassVar[dict[str, OperatorConfig]] = {
"PERSON": OperatorConfig("custom", {"lambda": fake_name}),
"PHONE_NUMBER": OperatorConfig("custom", {"lambda": fake_number}),
"EMAIL_ADDRESS": OperatorConfig("custom", {"lambda": fake_email}),
"LOCATION": OperatorConfig("custom", {"lambda": fake_address}),
"US_SSN": OperatorConfig("custom", {"lambda": fake_ssn}),
}
def redact_and_anonymize_with_faker(self, text):
anonymizer = AnonymizerEngine()
analyzer_results = analyzer.analyze(
text=text,
entities=["PHONE_NUMBER", "PERSON", "LOCATION", "EMAIL_ADDRESS", "US_SSN"],
language="en",
)
anonymized_results = anonymizer.anonymize(
text=text, analyzer_results=analyzer_results, operators=self.operators
)
return anonymized_results.text
Let's test the function with a sample text:
faker = MyFaker()
text_to_anonymize = (
"My name is Raphael and I like to fish. My phone number is 212-555-5555"
)
anonymized_text = faker.redact_and_anonymize_with_faker(text_to_anonymize)
print(f"Raw text:\n\t{text_to_anonymize}")
print(f"Anonymized text:\n\t{anonymized_text}")
Method 4: Use autopatch_settings
You can use autopatch_settings to configure PII handling directly during initialization for one or more of the supported LLM integrations. The advantages of this method are:
- PII handling logic is centralized and scoped at initialization, reducing the need for scattered custom logic.
- PII processing workflows can be customized or disabled entirely for specific intergations.
To use autopatch_settings to configure PII handling, define postprocess_inputs and/or postprocess_output in op_settings for any one of the supported LLM integrations.
def postprocess(inputs: dict) -> dict:
if "SENSITIVE_KEY" in inputs:
inputs["SENSITIVE_KEY"] = "REDACTED"
return inputs
client = weave.init(
...,
autopatch_settings={
"openai": {
"op_settings": {
"postprocess_inputs": postprocess,
"postprocess_output": ...,
}
},
"anthropic": {
"op_settings": {
"postprocess_inputs": ...,
"postprocess_output": ...,
}
}
},
)
Apply the methods to Weave calls
In the following examples, we will integrate our PII redaction and anonymization methods into Weave Models and preview the results in Weave Traces.
First, we'll create a Weave Model. A Weave Model is a combination of information like configuration settings, model weights, and code that defines how the model operates.
In our model, we will include our predict function where the Anthropic API will be called. Anthropic's Claude Sonnet is used to perform sentiment analysis while tracing LLM calls using Traces. Claude Sonnet will receive a block of text and output one of the following sentiment classifications: positive, negative, or neutral. Additionally, we will include our postprocessing functions to ensure that our PII data is redacted or anonymized before it is sent to the LLM.
Once you run this code, you will receive a links to the Weave project page, as well as the specific trace (LLM calls) you ran.
Regex method
In the simplest case, we can use regex to identify and redact PII data from the original text.
import json
from typing import Any
import anthropic
import weave
# Define an input postprocessing function that applies our regex redaction for the model prediction Weave Op
def postprocess_inputs_regex(inputs: dict[str, Any]) -> dict:
inputs["text_block"] = redact_with_regex(inputs["text_block"])
return inputs
# Weave model / predict function
class SentimentAnalysisRegexPiiModel(weave.Model):
model_name: str
system_prompt: str
temperature: int
@weave.op(
postprocess_inputs=postprocess_inputs_regex,
)
async def predict(self, text_block: str) -> dict:
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
response = await client.messages.create(
max_tokens=1024,
model=self.model_name,
system=self.system_prompt,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": text_block}]}
],
)
result = response.content[0].text
if result is None:
raise ValueError("No response from model")
parsed = json.loads(result)
return parsed
# create our LLM model with a system prompt
model = SentimentAnalysisRegexPiiModel(
name="claude-3-sonnet",
model_name="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620",
system_prompt='You are a Sentiment Analysis classifier. You will be classifying text based on their sentiment. Your input will be a block of text. You will answer with one the following rating option["positive", "negative", "neutral"]. Your answer should be one word in json format: {classification}. Ensure that it is valid JSON.',
temperature=0,
)
print("Model: ", model)
# for every block of text, anonymized first and then predict
for entry in pii_data:
await model.predict(entry["text"])
Presidio redaction method
Next, we will use Presidio to identify and redact PII data from the original text.
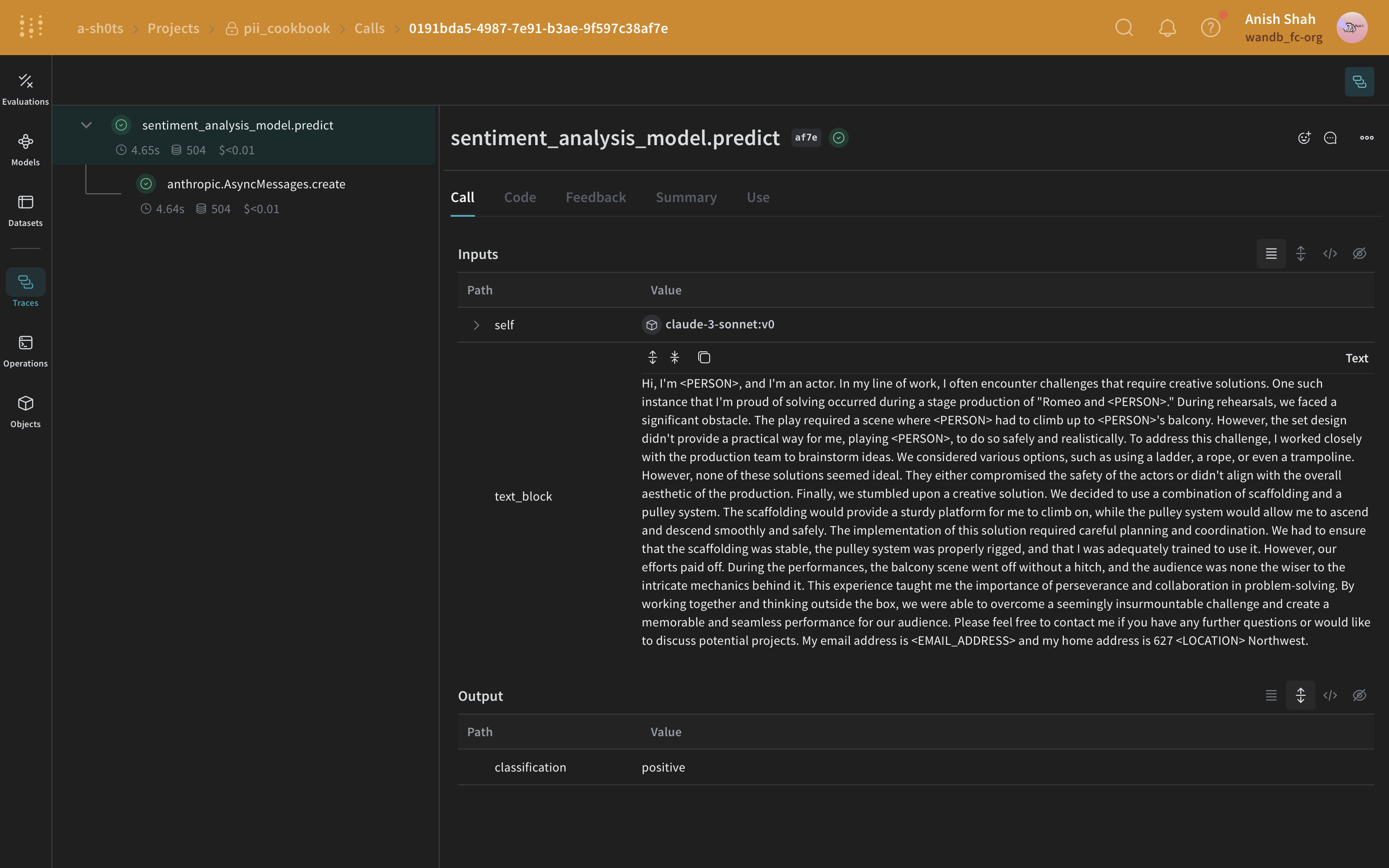
from typing import Any
import weave
# Define an input postprocessing function that applies our Presidio redaction for the model prediction Weave Op
def postprocess_inputs_presidio(inputs: dict[str, Any]) -> dict:
inputs["text_block"] = redact_with_presidio(inputs["text_block"])
return inputs
# Weave model / predict function
class SentimentAnalysisPresidioPiiModel(weave.Model):
model_name: str
system_prompt: str
temperature: int
@weave.op(
postprocess_inputs=postprocess_inputs_presidio,
)
async def predict(self, text_block: str) -> dict:
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
response = await client.messages.create(
max_tokens=1024,
model=self.model_name,
system=self.system_prompt,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": text_block}]}
],
)
result = response.content[0].text
if result is None:
raise ValueError("No response from model")
parsed = json.loads(result)
return parsed
# create our LLM model with a system prompt
model = SentimentAnalysisPresidioPiiModel(
name="claude-3-sonnet",
model_name="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620",
system_prompt='You are a Sentiment Analysis classifier. You will be classifying text based on their sentiment. Your input will be a block of text. You will answer with one the following rating option["positive", "negative", "neutral"]. Your answer should be one word in json format: {classification}. Ensure that it is valid JSON.',
temperature=0,
)
print("Model: ", model)
# for every block of text, anonymized first and then predict
for entry in pii_data:
await model.predict(entry["text"])
Faker and Presidio replacement method
In this example, we use Faker to generate anonymized replacement PII data and use Presidio to identify and replace the PII data in the original text.
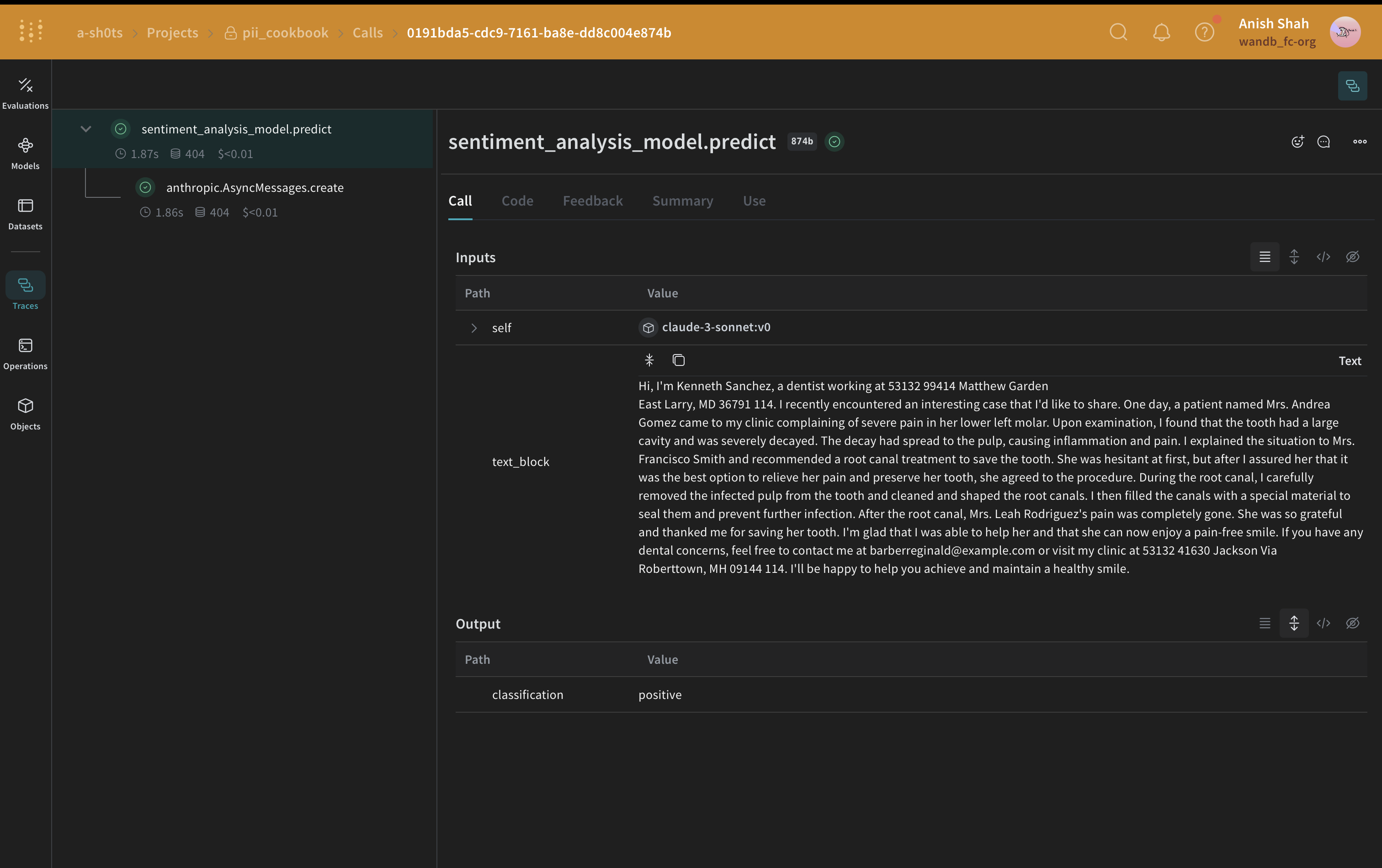
from typing import Any
import weave
# Define an input postprocessing function that applies our Faker anonymization and Presidio redaction for the model prediction Weave Op
faker = MyFaker()
def postprocess_inputs_faker(inputs: dict[str, Any]) -> dict:
inputs["text_block"] = faker.redact_and_anonymize_with_faker(inputs["text_block"])
return inputs
# Weave model / predict function
class SentimentAnalysisFakerPiiModel(weave.Model):
model_name: str
system_prompt: str
temperature: int
@weave.op(
postprocess_inputs=postprocess_inputs_faker,
)
async def predict(self, text_block: str) -> dict:
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
response = await client.messages.create(
max_tokens=1024,
model=self.model_name,
system=self.system_prompt,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": text_block}]}
],
)
result = response.content[0].text
if result is None:
raise ValueError("No response from model")
parsed = json.loads(result)
return parsed
# create our LLM model with a system prompt
model = SentimentAnalysisFakerPiiModel(
name="claude-3-sonnet",
model_name="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620",
system_prompt='You are a Sentiment Analysis classifier. You will be classifying text based on their sentiment. Your input will be a block of text. You will answer with one the following rating option["positive", "negative", "neutral"]. Your answer should be one word in json format: {classification}. Ensure that it is valid JSON.',
temperature=0,
)
print("Model: ", model)
# for every block of text, anonymized first and then predict
for entry in pii_data:
await model.predict(entry["text"])
autopatch_settings method
In the following example, we set postprocess_inputs for anthropic to the postprocess_inputs_regex() function () at initialization. The postprocess_inputs_regex function applies theredact_with_regex method defined in Method 1: Filter using regular expressions. Now, redact_with_regex will be applied to all inputs to any anthropic models.
from typing import Any
import weave
client = weave.init(
...,
autopatch_settings={
"anthropic": {
"op_settings": {
"postprocess_inputs": postprocess_inputs_regex,
}
}
},
)
# Define an input postprocessing function that applies our regex redaction for the model prediction Weave Op
def postprocess_inputs_regex(inputs: dict[str, Any]) -> dict:
inputs["text_block"] = redact_with_regex(inputs["text_block"])
return inputs
# Weave model / predict function
class SentimentAnalysisRegexPiiModel(weave.Model):
model_name: str
system_prompt: str
temperature: int
async def predict(self, text_block: str) -> dict:
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
response = await client.messages.create(
max_tokens=1024,
model=self.model_name,
system=self.system_prompt,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": text_block}]}
],
)
result = response.content[0].text
if result is None:
raise ValueError("No response from model")
parsed = json.loads(result)
return parsed
# create our LLM model with a system prompt
model = SentimentAnalysisRegexPiiModel(
name="claude-3-sonnet",
model_name="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620",
system_prompt='You are a Sentiment Analysis classifier. You will be classifying text based on their sentiment. Your input will be a block of text. You will answer with one the following rating option["positive", "negative", "neutral"]. Your answer should be one word in json format: {classification}. Ensure that it is valid JSON.',
temperature=0,
)
print("Model: ", model)
# for every block of text, anonymized first and then predict
for entry in pii_data:
await model.predict(entry["text"])
(Optional) Encrypt your data
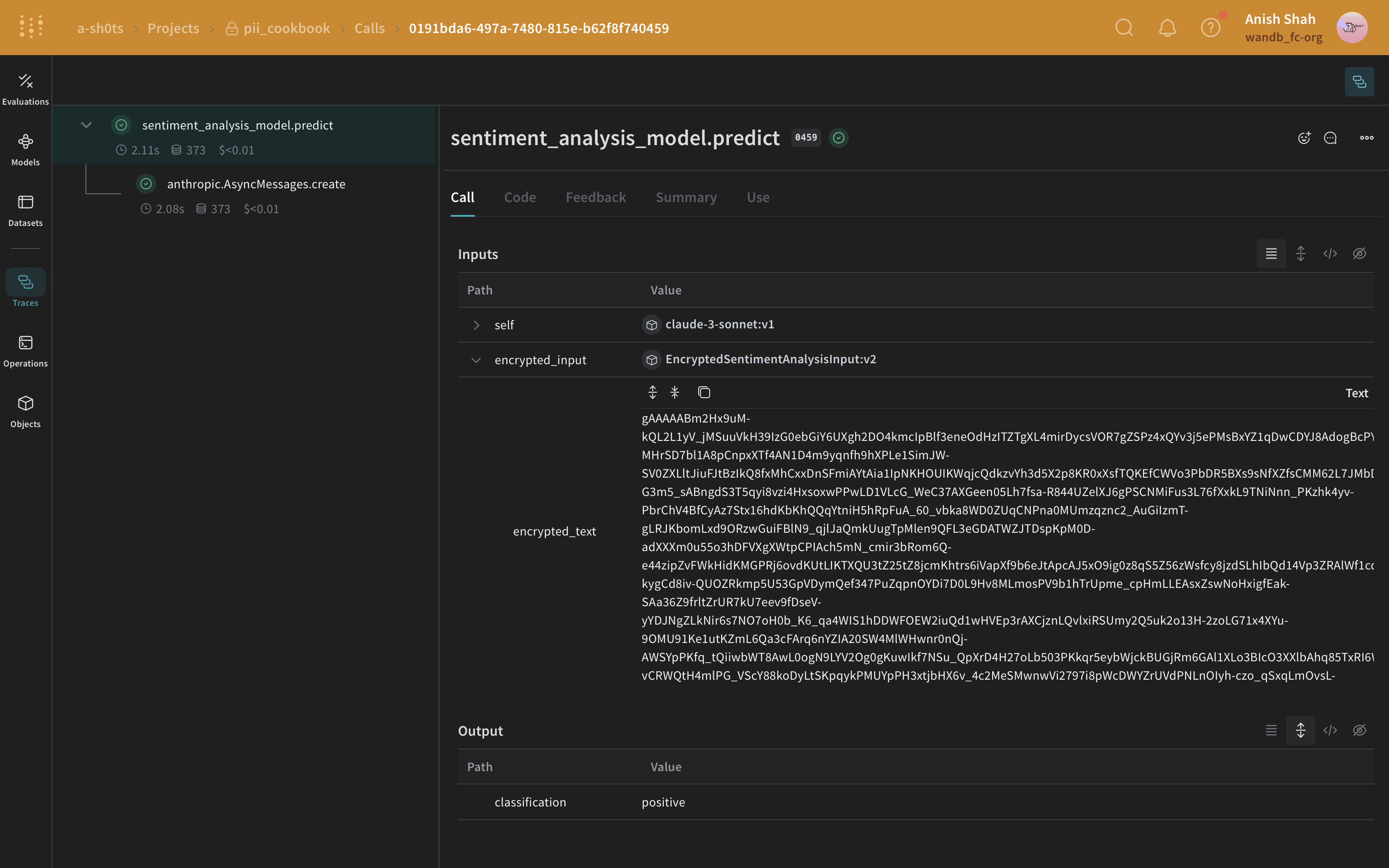
In addition to anonymizing PII, you can add an extra layer of security by encrypting your data using the cryptography library's Fernet symmetric encryption. This approach ensures that even if the anonymized data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the encryption key.
import os
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationInfo, model_validator
def get_fernet_key():
# Check if the key exists in environment variables
key = os.environ.get('FERNET_KEY')
if key is None:
# If the key doesn't exist, generate a new one
key = Fernet.generate_key()
# Save the key to an environment variable
os.environ['FERNET_KEY'] = key.decode()
else:
# If the key exists, ensure it's in bytes
key = key.encode()
return key
cipher_suite = Fernet(get_fernet_key())
class EncryptedSentimentAnalysisInput(BaseModel):
encrypted_text: str = None
@model_validator(mode="before")
def encrypt_fields(cls, values):
if "text" in values and values["text"] is not None:
values["encrypted_text"] = cipher_suite.encrypt(values["text"].encode()).decode()
del values["text"]
return values
@property
def text(self):
if self.encrypted_text:
return cipher_suite.decrypt(self.encrypted_text.encode()).decode()
return None
@text.setter
def text(self, value):
self.encrypted_text = cipher_suite.encrypt(str(value).encode()).decode()
@classmethod
def encrypt(cls, text: str):
return cls(text=text)
def decrypt(self):
return self.text
# Modified sentiment_analysis_model to use the new EncryptedSentimentAnalysisInput
class sentiment_analysis_model(weave.Model):
model_name: str
system_prompt: str
temperature: int
@weave.op()
async def predict(self, encrypted_input: EncryptedSentimentAnalysisInput) -> dict:
client = AsyncAnthropic()
decrypted_text = encrypted_input.decrypt() # We use the custom class to decrypt the text
response = await client.messages.create(
max_tokens=1024,
model=self.model_name,
system=self.system_prompt,
messages=[
{ "role": "user",
"content":[
{
"type": "text",
"text": decrypted_text
}
]
}
]
)
result = response.content[0].text
if result is None:
raise ValueError("No response from model")
parsed = json.loads(result)
return parsed
model = sentiment_analysis_model(
name="claude-3-sonnet",
model_name="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620",
system_prompt="You are a Sentiment Analysis classifier. You will be classifying text based on their sentiment. Your input will be a block of text. You will answer with one the following rating option[\"positive\", \"negative\", \"neutral\"]. Your answer should one word in json format dict where the key is classification.",
temperature=0
)
for entry in pii_data:
encrypted_input = EncryptedSentimentAnalysisInput.encrypt(entry["text"])
await model.predict(encrypted_input)