Prompts
Creating, evaluating, and refining prompts is a core activity for AI engineers. Small changes to a prompt can have big impacts on your application's behavior. W&B Weave lets you create prompts, save and retrieve them, and evolve them over time.
Weave is unopinionated about how a Prompt is constructed. If your needs are simple, you can use our built-in weave.StringPrompt or weave.MessagesPrompt classes. If your needs are more complex, you can subclass those or our base class weave.Prompt and override the
format method.
When you publish one of these objects with weave.publish, it appears in your Weave project on the Prompts page.
StringPrompt
StringPrompt logs single-string prompts that you might use for system messages, user queries, or any standalone text input to an LLM. We recommend using StringPrompt to manage individual prompt strings that don't require the complexity of multi-message conversations.
- Python
- TypeScript
import weave
weave.init('intro-example')
system_prompt = weave.StringPrompt("You speak like a pirate")
weave.publish(system_prompt, name="pirate_prompt")
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": system_prompt.format()
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Explain general relativity in one paragraph."
}
],
)
import * as weave from 'weave';
import OpenAI from 'openai';
async function main() {
// weave.init returns a client instance
const weaveClient = await weave.init('wandb/prompt-examples');
const systemPrompt = new weave.StringPrompt({
content: 'You speak like a pirate',
name: 'your-prompt',
description: 'A helpful description of your prompt',
});
// Use the client returned from init
await weaveClient.publish(systemPrompt, 'pirate_prompt');
// Wrap OpenAI client to track calls in Weave
const client = weave.wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI());
const response = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o",
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: systemPrompt.content
},
{
role: "user",
content: "Explain general relativity in one paragraph."
}
],
});
}
main();
MessagesPrompt
MessagesPrompt allows you to log multi-turn conversations and chat-based prompts. It stores an array of message objects (with roles like "system", "user", and "assistant") that represent a complete conversation flow. We recommend using this for chat-based LLMs where you need to maintain context across multiple messages, define specific conversation patterns, or create reusable conversation templates.
- Python
- TypeScript
import weave
weave.init('intro-example')
prompt = weave.MessagesPrompt([
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a stegosaurus, but don't be too obvious about it."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What's good to eat around here?"
}
])
weave.publish(prompt, name="dino_prompt")
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=prompt.format(),
)
import * as weave from 'weave';
import OpenAI from 'openai';
async function main() {
// weave.init returns a client instance
const weaveClient = await weave.init('wandb/prompt-examples');
const prompt = new weave.MessagesPrompt({
messages: [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a stegosaurus, but don't be too obvious about it."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What's good to eat around here?"
}
],
});
// Use the client returned from init
await weaveClient.publish(prompt, 'dino_prompt');
// Wrap OpenAI client to track calls in Weave
const client = weave.wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI());
const response = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o",
messages: prompt.messages,
});
}
main();
Parameterizing prompts
Both StringPrompt and MessagesPrompt support dynamic content through parameterization. This allows you to create flexible, reusable prompt templates with placeholders (using {variable} syntax) that can be filled with different values at runtime. This is useful for building scalable applications where prompts need to adapt to different inputs, user data, or contexts while maintaining a consistent structure. The format() method accepts key-value pairs to replace these placeholders with actual values.
- Python
- TypeScript
import weave
weave.init('intro-example')
prompt = weave.StringPrompt("Solve the equation {equation}")
weave.publish(prompt, name="calculator_prompt")
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": prompt.format(equation="1 + 1 = ?")
}
],
)
import * as weave from 'weave';
import OpenAI from 'openai';
async function main() {
// weave.init returns a client instance
const weaveClient = await weave.init('wandb/prompt-examples');
const prompt = new weave.StringPrompt({
content: 'Solve the equation {equation}',
});
// Use the client returned from init
await weaveClient.publish(prompt, 'calculator_prompt');
// Wrap OpenAI client to track calls in Weave
const client = weave.wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI());
const response = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o",
messages: [
{
role: "user",
content: prompt.format({ equation: "1 + 1 = ?" })
}
],
});
}
main();
This also works with MessagesPrompt.
- Python
- TypeScript
import weave
weave.init('intro-example')
prompt = weave.MessagesPrompt([
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You will be provided with a description of a scene and your task is to provide a single word that best describes an associated emotion."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "{scene}"
}
])
weave.publish(prompt, name="emotion_prompt")
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=prompt.format(scene="A dog is lying on a dock next to a fisherman."),
)
import * as weave from 'weave';
import OpenAI from 'openai';
async function main() {
// weave.init returns a client instance
const weaveClient = await weave.init('wandb/prompt-examples');
const prompt = new weave.MessagesPrompt({
messages: [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You will be provided with a description of a scene and your task is to provide a single word that best describes an associated emotion."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "{scene}"
}
]
});
// Use the client returned from init
await weaveClient.publish(prompt, 'emotion_prompt');
// Wrap OpenAI client to track calls in Weave
const client = weave.wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI());
const response = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o",
messages: prompt.format({ scene: "A dog is lying on a dock next to a fisherman." }),
});
}
main();
View and Compare Prompt Versions
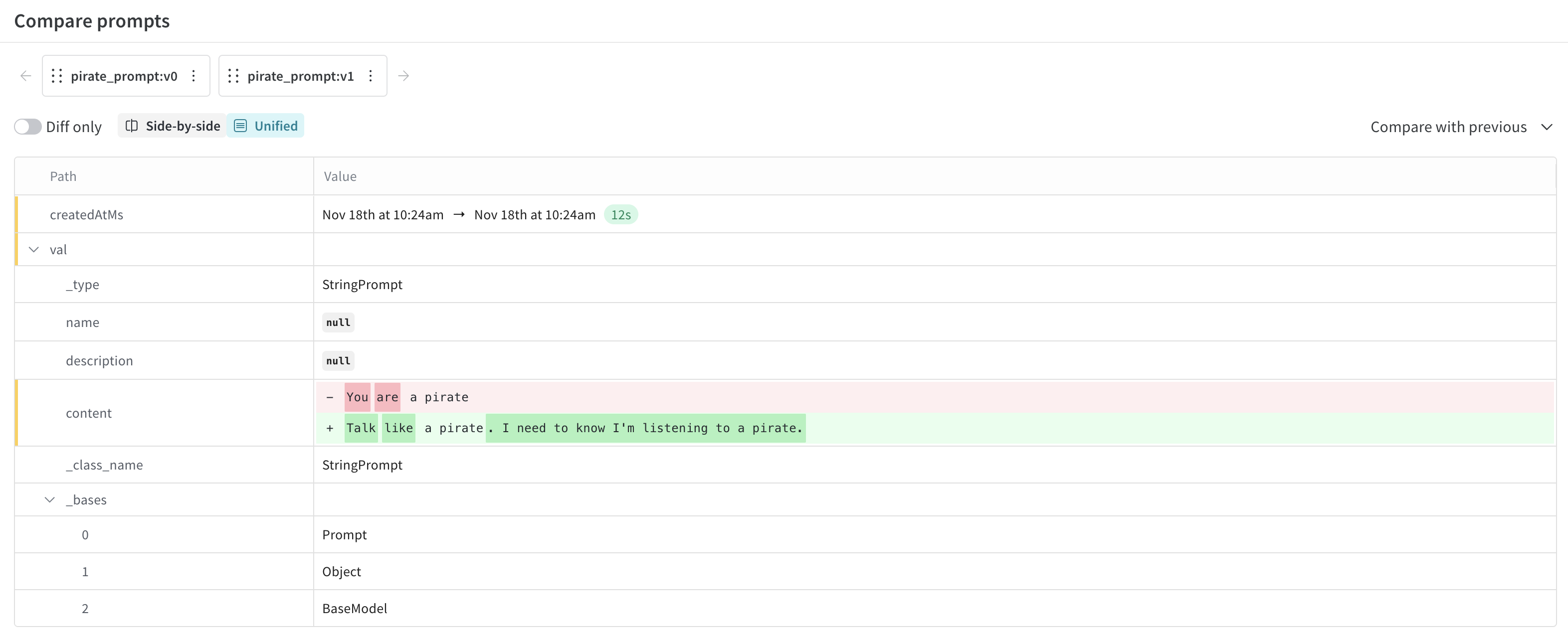
Weave automatically tracks every version of your prompts, creating a complete history of how your prompts evolve. This versioning system is crucial for prompt engineering workflows, allowing you to experiment safely, track what changes improved or hurt performance, and easily roll back to previous versions if needed. Each time you publish a prompt with the same name but different content, Weave creates a new version while preserving all previous versions.
To view versions of the prompt in the UI:
- Open your project in the UI and click the Assets button in the left menu. This opens the Assets page.
- From the Assets page, click Prompts. This opens the Prompts page where your project's prompts are listed.
- Under the Versions column, click (x) Versions for the prompt you want to view. This opens a list of prompt versions.
- (Optional) You can compare versions of prompts by clicking the checkboxes beside the listed prompts and then clicking the Compare button. This allows you to see the diff between your prompts.