Amazon Bedrock
Weave automatically tracks and logs LLM calls made via Amazon Bedrock, AWS's fully managed service that offers foundation models from leading AI companies through a unified API.
There are multiple ways to log LLM calls to Weave from Amazon Bedrock. You can use weave.op to create reusable operations for tracking any calls to a Bedrock model. Optionally, if you're using Anthropic models, you can use Weave’s built-in integration with Anthropic.
For the latest tutorials, visit Weights & Biases on Amazon Web Services.
Traces
Weave will automatically capture traces for Bedrock API calls after you initialize Weave and patch the client.
To use the Bedrock API:
import weave
import boto3
import json
from weave.integrations.bedrock.bedrock_sdk import patch_client
weave.init("my_bedrock_app")
# Create and patch the Bedrock client
client = boto3.client("bedrock-runtime")
patch_client(client)
# Use the client as usual
response = client.invoke_model(
modelId="anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620-v1:0",
body=json.dumps({
"anthropic_version": "bedrock-2023-05-31",
"max_tokens": 100,
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the capital of France?"}
]
}),
contentType='application/json',
accept='application/json'
)
response_dict = json.loads(response.get('body').read())
print(response_dict["content"][0]["text"])
To use the converse API:
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": [{"text": "What is the capital of France?"}]}]
response = client.converse(
modelId="anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620-v1:0",
system=[{"text": "You are a helpful AI assistant."}],
messages=messages,
inferenceConfig={"maxTokens": 100},
)
print(response["output"]["message"]["content"][0]["text"])
Wrapping with your own ops
You can create reusable operations using the @weave.op() decorator. Here's an example showing both the invoke_model and converse APIs:
@weave.op
def call_model_invoke(
model_id: str,
prompt: str,
max_tokens: int = 100,
temperature: float = 0.7
) -> dict:
body = json.dumps({
"anthropic_version": "bedrock-2023-05-31",
"max_tokens": max_tokens,
"temperature": temperature,
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
})
response = client.invoke_model(
modelId=model_id,
body=body,
contentType='application/json',
accept='application/json'
)
return json.loads(response.get('body').read())
@weave.op
def call_model_converse(
model_id: str,
messages: str,
system_message: str,
max_tokens: int = 100,
) -> dict:
response = client.converse(
modelId=model_id,
system=[{"text": system_message}],
messages=messages,
inferenceConfig={"maxTokens": max_tokens},
)
return response
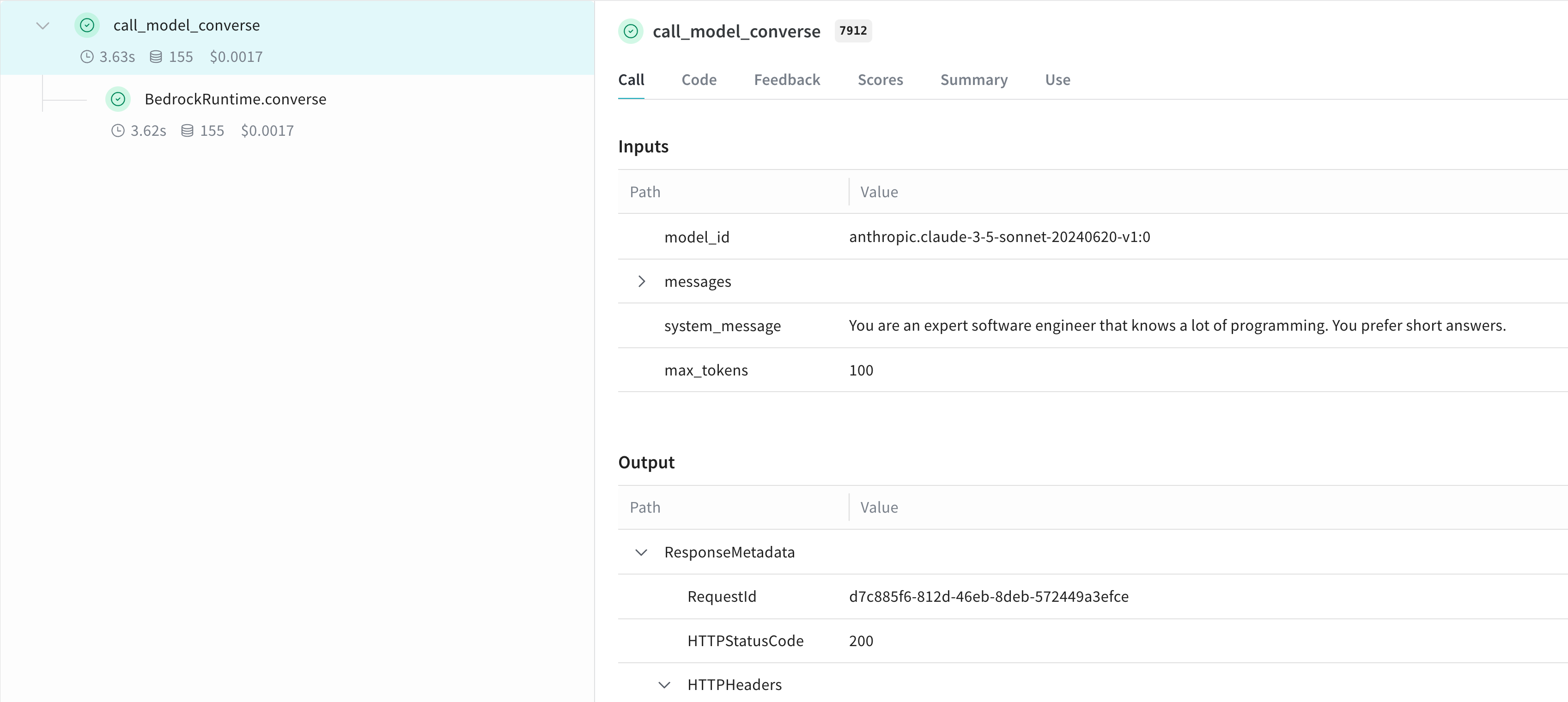
Create a Model for easier experimentation
You can create a Weave Model to better organize your experiments and capture parameters. Here's an example using the converse API:
class BedrockLLM(weave.Model):
model_id: str
max_tokens: int = 100
system_message: str = "You are a helpful AI assistant."
@weave.op
def predict(self, prompt: str) -> str:
"Generate a response using Bedrock's converse API"
messages = [{
"role": "user",
"content": [{"text": prompt}]
}]
response = client.converse(
modelId=self.model_id,
system=[{"text": self.system_message}],
messages=messages,
inferenceConfig={"maxTokens": self.max_tokens},
)
return response["output"]["message"]["content"][0]["text"]
# Create and use the model
model = BedrockLLM(
model_id="anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620-v1:0",
max_tokens=100,
system_message="You are an expert software engineer that knows a lot of programming. You prefer short answers."
)
result = model.predict("What is the best way to handle errors in Python?")
print(result)
This approach allows you to version your experiments and easily track different configurations of your Bedrock-based application.
Learn more
Learn more about using Amazon Bedrock with Weave
Try Bedrock in the Weave Playground
Do you want to experiment with Amazon Bedrock models in the Weave UI without any set up? Try the LLM Playground.
Report: Compare LLMs on Bedrock for text summarization with Weave
The Compare LLMs on Bedrock for text summarization with Weave report explains how to use Bedrock in combination with Weave to evaluate and compare LLMs for summarization tasks, code samples included.