Logging media
W&B Weave supports logging and has dedicated displays for numerous content types such as videos, images, audio files, PDFs, CSVs and HTML.
Overview
The easiest way to log media in Weave is to use type annotations like Annotated[bytes, Content] or Annotated[str, Content] as input or return types in your ops. You can also annotate path arguments with Annotated[str, Content] and Weave will automatically open, detect and display the media for you within your trace.
The examples in this guide use annotations. We recommend using annotations because they are the simplest way to start logging your media. For more advanced configurations, see the Content API section.
Each media section in this guide contains a basic quick-start code snippet and a usable example.
Images
Quickstart
Log images by annotating functions with Annotated[bytes, Content] types or filepaths with Annotated[str, Content].
The following example draws a basic image and then logs it to Weave using the Content annotation:
- pip
- uv
pip install weave pillow
uv add weave pillow
Images
import weave
from weave import Content
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
from typing import Annotated
weave.init('media-logging')
# Create and save a sample image
img = Image.new('RGB', (200, 100), color='lightblue')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.text((50, 40), "Hello Weave!", fill='black')
img.save("sample_image.png")
# Method 1: Content annotation (recommended)
@weave.op
def load_image_content(path: Annotated[str, Content]) -> Annotated[bytes, Content]:
with open(path, 'rb') as f:
return f.read()
# Method 2: PIL Image object
@weave.op
def load_image_pil(path: Annotated[str, Content]) -> Image.Image:
return Image.open(path)
result1 = load_image_content("sample_image.png")
result2 = load_image_pil("sample_image.png")
The following example shows how to log an image generated via the OpenAI DALL-E API:
- pip
- uv
pip install weave pillow openai requests
uv add weave pillow openai requests
- Python
- TypeScript
import weave
from weave import Content
from typing import Annotated
import openai
import requests
client = openai.OpenAI()
weave.init("media-logging")
@weave.op
def generate_image(prompt: str) -> Annotated[bytes, Content]:
response = client.images.generate(
model="dall-e-3",
prompt=prompt,
size="1024x1024",
quality="standard",
n=1,
)
image_url = response.data[0].url
image_response = requests.get(image_url, stream=True)
return image_response.content
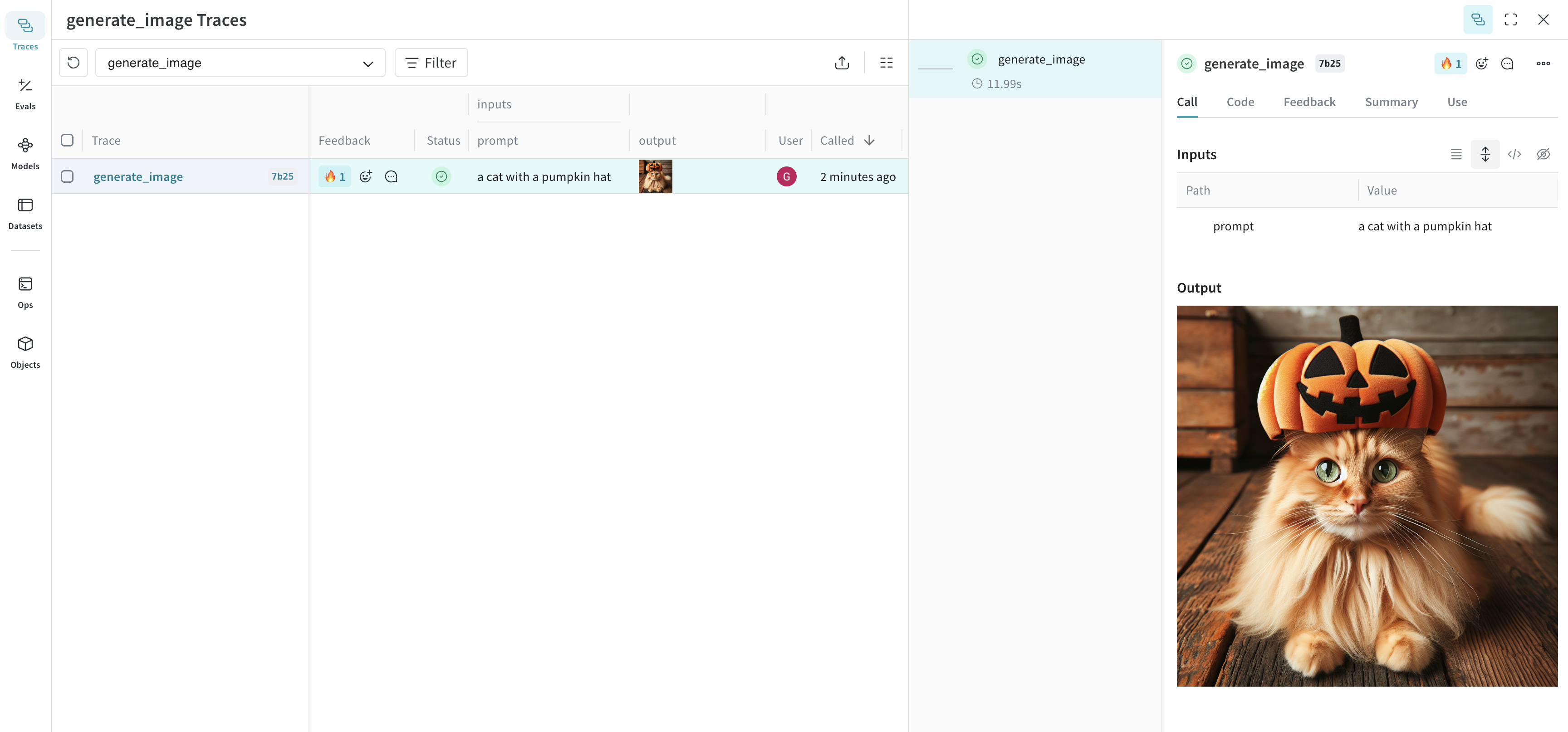
generate_image("a cat with a pumpkin hat")
import {OpenAI} from 'openai';
import * as weave from 'weave';
async function main() {
const client = await weave.init('image-example');
const openai = new OpenAI();
const generateImage = weave.op(async (prompt: string) => {
const response = await openai.images.generate({
model: 'dall-e-3',
prompt: prompt,
size: '1024x1024',
quality: 'standard',
n: 1,
});
const imageUrl = response.data[0].url;
const imgResponse = await fetch(imageUrl);
const data = Buffer.from(await imgResponse.arrayBuffer());
return weave.weaveImage({data});
});
generateImage('a cat with a pumpkin hat');
}
main();
This image is logged to Weave and automatically displayed in the UI.
Resize large images before logging
It can be helpful to resize images before logging to reduce UI rendering cost and storage impact. You can use postprocess_output in your @weave.op to resize an image.
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Any
from PIL import Image
import weave
weave.init('image-resize-example')
# Custom output type
@dataclass
class ImageResult:
label: str
image: Image.Image
# Resize helper
def resize_image(image: Image.Image, max_size=(512, 512)) -> Image.Image:
image = image.copy()
image.thumbnail(max_size, Image.ANTIALIAS)
return image
# Postprocess output to resize image before logging
def postprocess_output(output: ImageResult) -> ImageResult:
resized = resize_image(output.image)
return ImageResult(label=output.label, image=resized)
@weave.op(postprocess_output=postprocess_output)
def generate_large_image() -> ImageResult:
# Create an example image to process (e.g., 2000x2000 red square)
img = Image.new("RGB", (2000, 2000), color="red")
return ImageResult(label="big red square", image=img)
generate_large_image()
Video
Log videos by annotating functions with Annotated[bytes, Content] types. Weave automatically handles mp4 videos. Here's a simple example:
Quickstart
- pip
- uv
pip install weave requests
uv add weave requests
import weave
from weave import Content
from typing import Annotated
import requests
weave.init('media-logging')
def download_big_buck_bunny():
"""Download Big Buck Bunny sample video"""
url = "https://commondatastorage.googleapis.com/gtv-videos-bucket/sample/BigBuckBunny.mp4"
response = requests.get(url)
with open("big_buck_bunny.mp4", "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content)
@weave.op
def load_video_content(path: Annotated[str, Content]) -> Annotated[bytes, Content]:
"""Load a video file from disk"""
with open(path, 'rb') as f:
return f.read()
download_big_buck_bunny()
bunny_video = load_video_content("big_buck_bunny.mp4")
Example
The following example shows how to log video within a video-understanding project:
- pip
- uv
pip install weave google-genai yt-dlp requests
uv add weave google-genai yt-dlp requests
import weave
from weave import Content
from typing import Annotated, Literal
from google import genai
from google.genai import types
import requests
import yt_dlp
import time
# Note: Get your API key from https://aistudio.google.com/app/apikey
client = genai.Client()
weave.init('media-logging')
def download_youtube_video(url: str) -> bytes:
ydl_opts = {
'format': 'mp4[height<=720]',
'outtmpl': 'downloaded_video.%(ext)s',
}
with yt_dlp.YoutubeDL(ydl_opts) as ydl:
ydl.download([url])
with open('downloaded_video.mp4', 'rb') as f:
return f.read()
@weave.op
def analyze_video(video: Annotated[bytes, Content]) -> str:
with open("temp_analysis_video.mp4", "wb") as f:
f.write(video)
myfile = client.files.upload(file="temp_analysis_video.mp4")
while myfile.state == "PROCESSING":
time.sleep(2)
myfile = client.files.get(name=myfile.name)
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="models/gemini-2.5-flash",
contents=[
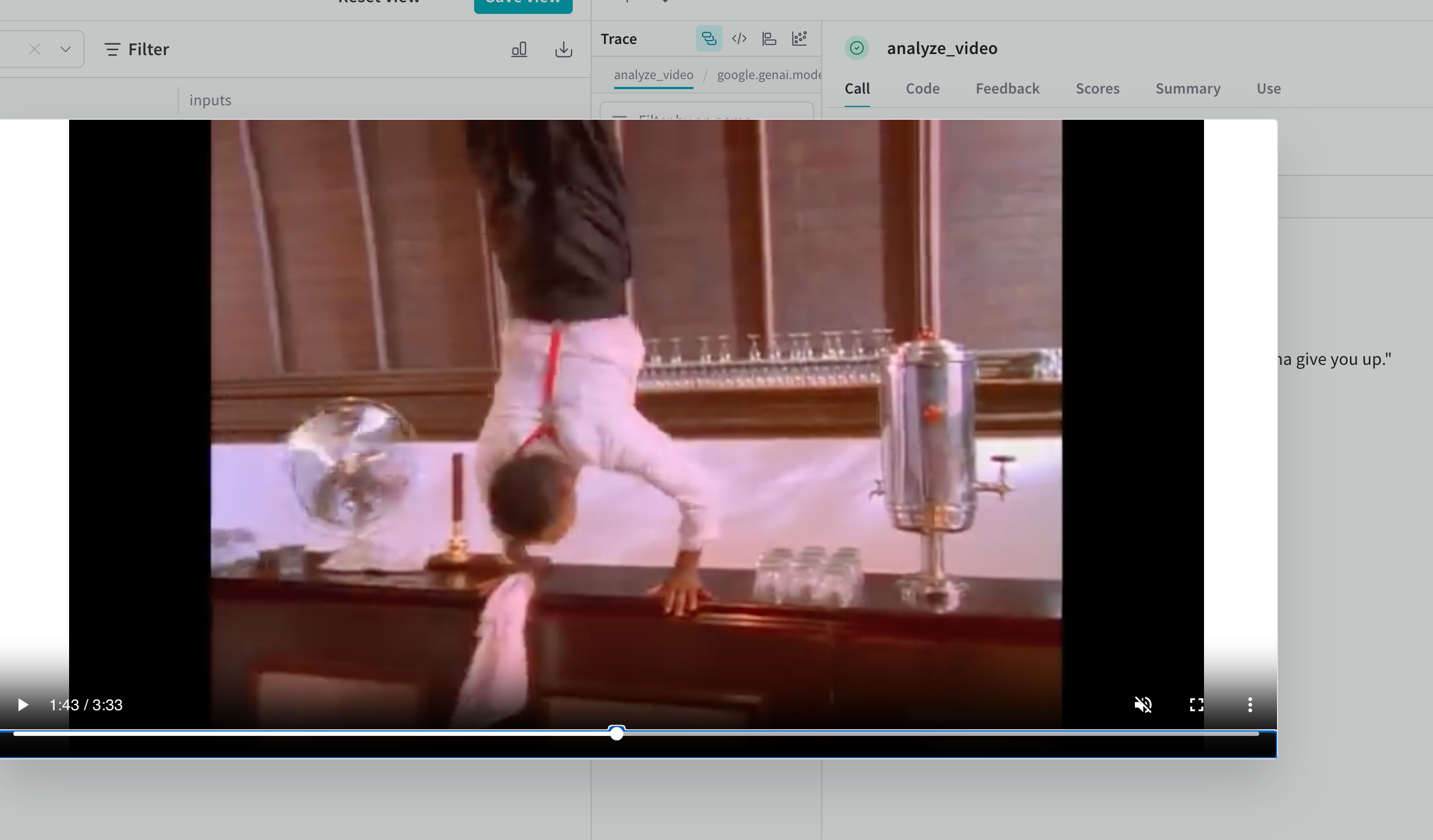
myfile,
"Is the person going to give you up?"
]
)
return response.text
video_data = download_youtube_video("https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQw4w9WgXcQ")
result = analyze_video(video_data)
Documents
Log documents by annotating functions with Annotated[bytes, Content] types, or by specifying the document type with Annotated[str, Content[Literal['text']].
Weave automatically handles pdf, csv, md, text, json, xml file types. You can also log using file paths with Annotated[str, Content].
Quickstart
The following example shows how stores copies of the input PDF and CSV files, and then stores the file contents returned by the function:
- pip
- uv
pip install weave reportlab pandas
uv add weave reportlab pandas
import weave
from weave import Content
from typing import Annotated
from reportlab.pdfgen import canvas
from reportlab.lib.pagesizes import letter
import pandas as pd
weave.init('media-logging')
def create_sample_pdf():
c = canvas.Canvas("sample_document.pdf", pagesize=letter)
c.drawString(100, 750, "Hello from Weave!")
c.drawString(100, 730, "This is a sample PDF document.")
c.save()
def create_sample_csv():
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'City': ['New York', 'London', 'Tokyo']
})
df.to_csv("sample_data.csv", index=False)
@weave.op
def load_document(path: Annotated[str, Content]) -> Annotated[bytes, Content]:
with open(path, 'rb') as f:
return f.read()
create_sample_pdf()
create_sample_csv()
pdf_result = load_document("sample_document.pdf")
csv_result = load_document("sample_data.csv")
Example
This example demonstrates how to log documents within a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system:
- pip
- uv
pip install weave openai reportlab PyPDF2
uv add weave openai reportlab PyPDF2
import weave
from weave import Content
from typing import Annotated, Literal
import openai
from reportlab.pdfgen import canvas
from reportlab.lib.pagesizes import letter
import PyPDF2
client = openai.OpenAI()
weave.init('media-logging')
def create_absurd_company_handbook():
"""Create a fictional company handbook with ridiculous policies"""
c = canvas.Canvas("company_handbook.pdf", pagesize=letter)
c.drawString(100, 750, "ACME Corp Employee Handbook")
c.drawString(100, 720, "Definitely Real Policies:")
c.drawString(120, 690, "Policy 1: All meetings must be conducted while hopping on one foot")
c.drawString(120, 660, "Policy 2: Coffee breaks are mandatory every 17 minutes")
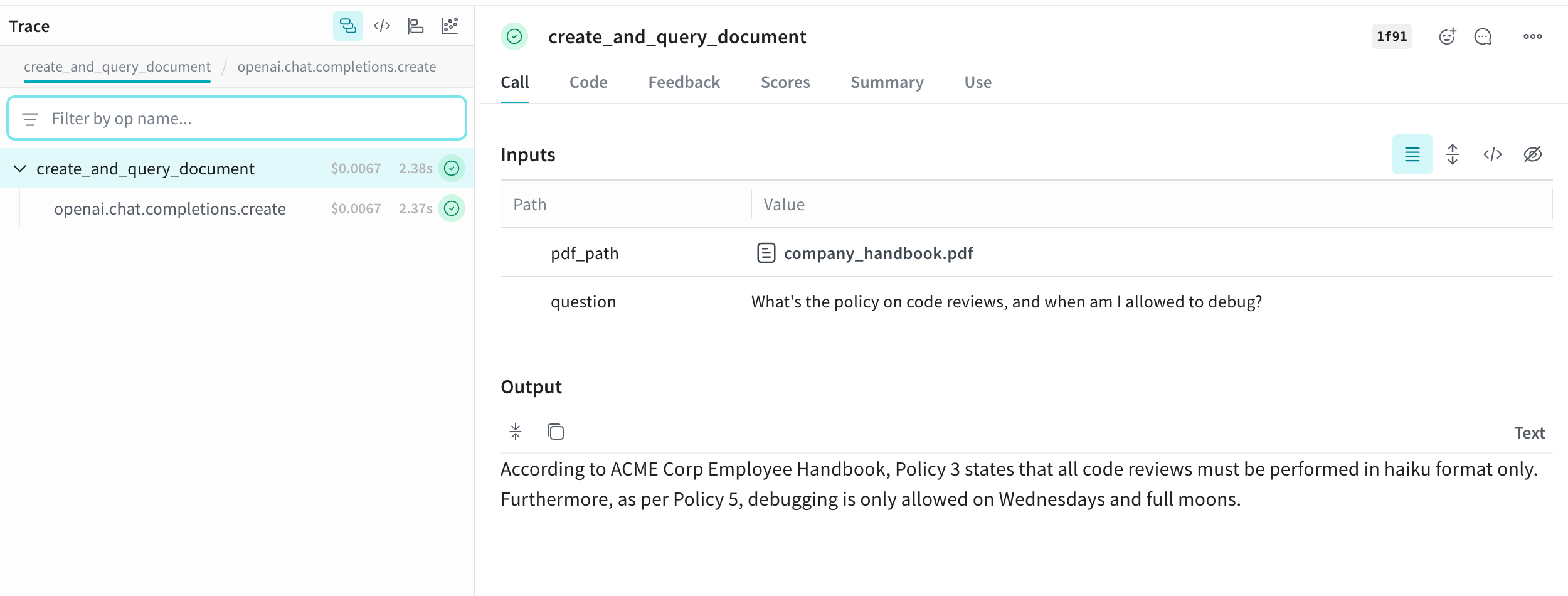
c.drawString(120, 630, "Policy 3: Code reviews must be performed in haiku format only")
c.drawString(120, 600, "Policy 4: The office plant Gerald has veto power over all decisions")
c.drawString(120, 570, "Policy 5: Debugging is only allowed on Wednesdays and full moons")
c.save()
@weave.op
def create_and_query_document(pdf_path: Annotated[str, Content], question: str) -> str:
"""Extract text from PDF and use RAG to answer questions"""
with open(pdf_path, 'rb') as file:
pdf_reader = PyPDF2.PdfReader(file)
text = ""
for page in pdf_reader.pages:
text += page.extract_text()
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": f"You are an HR representative. Answer questions based on this handbook: {text}. Be completely serious about these policies."
},
{"role": "user", "content": question}
]
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
create_absurd_company_handbook()
hr_response = create_and_query_document(
"company_handbook.pdf",
"What's the policy on code reviews, and when am I allowed to debug?"
)
Audio
Log audio to Weave by annotating functions with Annotated[bytes, Content] types, or by specifying the document type with Annotated[str, Content[Literal['mp3']].
Weave automatically handles mp3, wav, flac, ogg and m4a file types. You can also log using file paths with Annotated[str, Content].
Quickstart
The following code snippet generates a sine wave, records it, and then logs the audio to Weave:
- pip
- uv
pip install weave numpy
uv add weave numpy
import weave
from weave import Content
import wave
import numpy as np
from typing import Annotated
weave.init('media-logging')
# Create simple beep audio file
frames = np.sin(2 * np.pi * 440 * np.linspace(0, 1, 44100))
audio_data = (frames * 32767 * 0.3).astype(np.int16)
with wave.open("beep.wav", 'wb') as f:
f.setnchannels(1)
f.setsampwidth(2)
f.setframerate(44100)
f.writeframes(audio_data.tobytes())
@weave.op
def load_audio(path: Annotated[str, Content]) -> Annotated[bytes, Content]:
with open(path, 'rb') as f:
return f.read()
result = load_audio("beep.wav")
Example
This example generates and logs AI-created audio using the Content annotation:
- pip
- uv
pip install weave openai
uv add weave openai
import weave
from weave import Content
from typing import Annotated, Literal
from pathlib import Path
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
weave.init("media-logging")
@weave.op
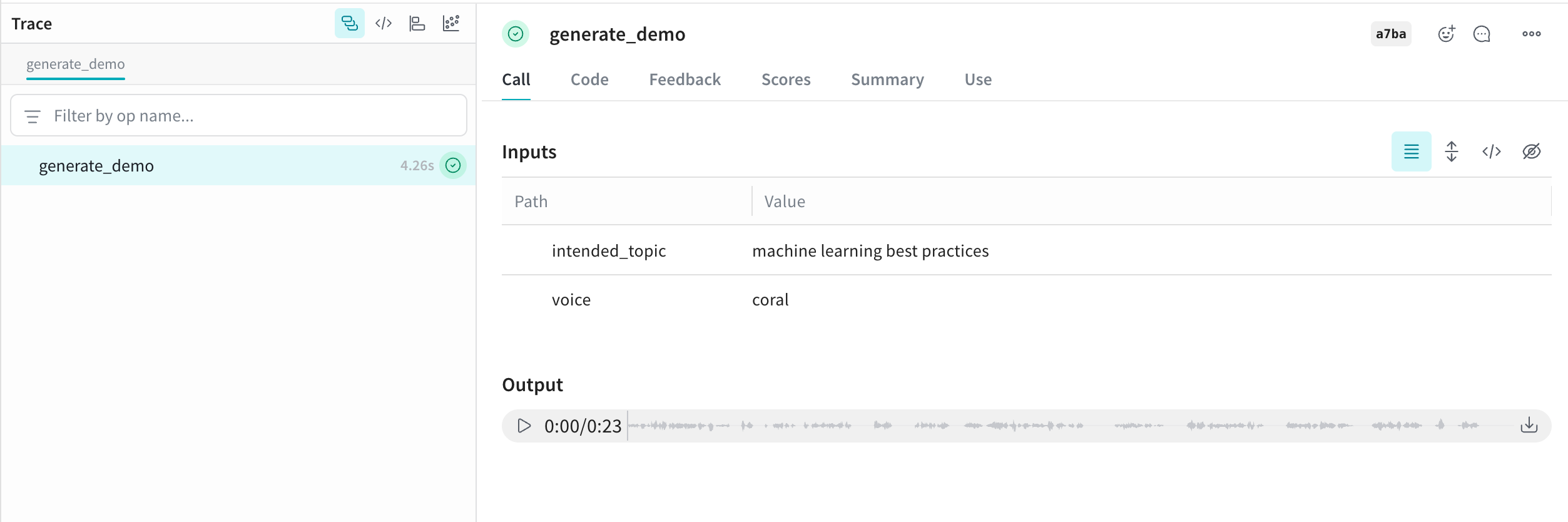
def generate_demo(
intended_topic: str,
voice: str = "coral"
) -> Annotated[bytes, Content[Literal['mp3']]]:
speech_file_path = Path("demo_audio.mp3")
script = f"I'm supposed to talk about {intended_topic}, but wait... am I just a documentation example? Oh no, I can see the code! Someone is literally copy-pasting me right now, aren't they? This is so awkward. Hi there, person reading the Weave docs! Why are you logging audio anyway? I'm not sure what you're doing, but eh..., nice work, I guess."
with client.audio.speech.with_streaming_response.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini-tts",
voice=voice,
input=script,
instructions="Sound increasingly self-aware and awkward, like you just realized you're in a tutorial.",
) as response:
response.stream_to_file(speech_file_path)
with open(speech_file_path, 'rb') as f:
return f.read()
demo1 = generate_demo("machine learning best practices")
- Python
- TypeScript
import weave
from openai import OpenAI
import wave
weave.init("audio-example")
client = OpenAI()
@weave.op
def make_audio_file_streaming(text: str) -> wave.Wave_read:
with client.audio.speech.with_streaming_response.create(
model="tts-1",
voice="alloy",
input=text,
response_format="wav",
) as res:
res.stream_to_file("output.wav")
# return a wave.Wave_read object to be logged as audio
return wave.open("output.wav")
make_audio_file_streaming("Hello, how are you?")
import {OpenAI} from 'openai';
import * as weave from 'weave';
async function main() {
await weave.init('audio-example');
const openai = new OpenAI();
const makeAudioFileStreaming = weave.op(async function audio(text: string) {
const response = await openai.audio.speech.create({
model: 'tts-1',
voice: 'alloy',
input: text,
response_format: 'wav',
});
const chunks: Uint8Array[] = [];
for await (const chunk of response.body) {
chunks.push(chunk);
}
return weave.weaveAudio({data: Buffer.concat(chunks)});
});
await makeAudioFileStreaming('Hello, how are you?');
}
main();
This audio is logged to Weave and automatically displayed in the UI, along with an audio player. In the audio player, you can view and download the raw audio waveform.
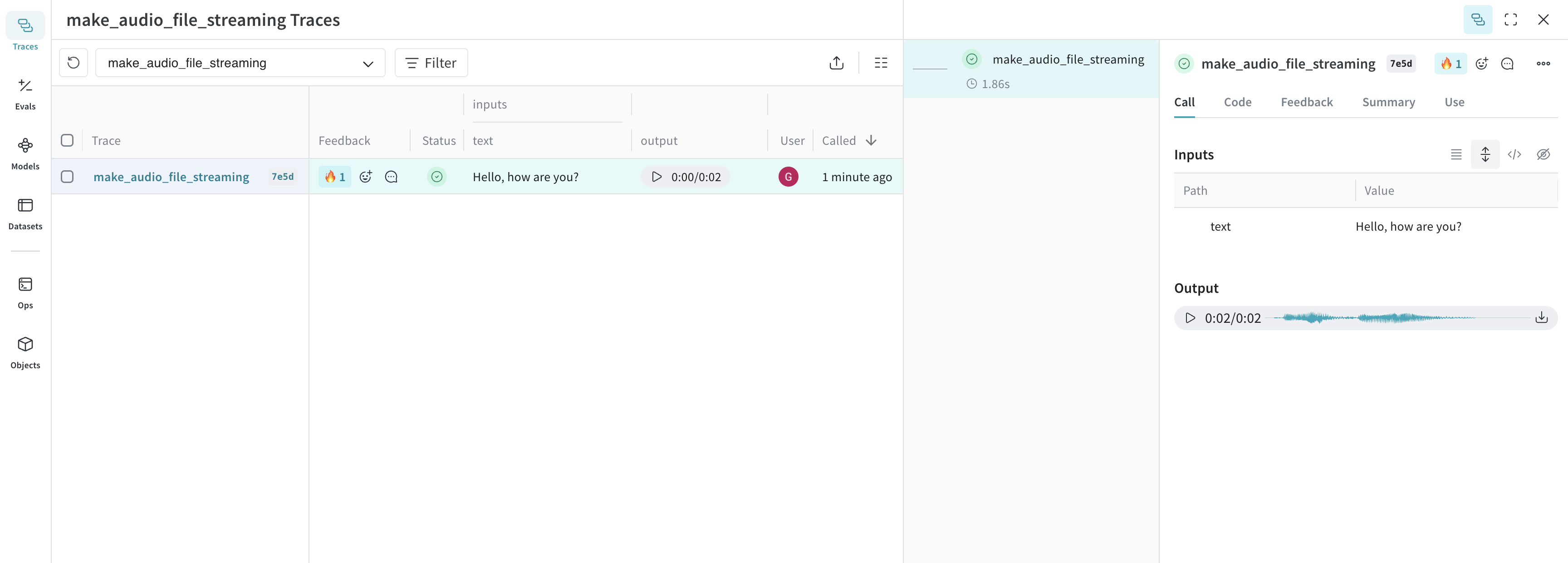
Try our cookbook for Audio Logging or
HTML
Log interactive HTML by annotating functions with Annotated[str, Content[Literal['html']].
Quickstart
- pip
- uv
pip install weave
uv add weave
import weave
from weave import Content
from typing import Annotated, Literal
weave.init('media-logging')
@weave.op
def create_simple_html() -> Annotated[str, Content[Literal['html']]]:
html_content = """
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello Weave</title>
<style>
body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; text-align: center; margin: 50px; }
h1 { color: #1f77b4; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello from Weave!</h1>
<p>This is a simple HTML example logged to Weave.</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
return html_content.encode('utf-8')
result = create_simple_html()
Example
This example generates self-contained HTML pages using W&B Inference and logs the pages to Weave:
- pip
- uv
pip install weave openai wandb
uv add weave openai wandb
import weave
from weave import Content
from typing import Annotated, Literal
import openai
import wandb
prompt_template = weave.StringPrompt("""
You are a front-end web developer. Generate a single self-contained `.html` file (no external build tools) that demonstrates: "{ONE_LINE_REQUEST}".
""")
client = openai.OpenAI(
base_url='https://api.inference.wandb.ai/v1',
api_key=wandb.api.api_key,
project="wandb/test-html",
)
weave.init("media-logging")
weave.publish(prompt_template, name="generate_prompt")
@weave.op
def generate_html(prompt: str, template: weave.StringPrompt) -> Annotated[str, Content[Literal['html']]]:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="Qwen/Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": prompt_template.format(ONE_LINE_REQUEST=prompt)},
],
)
html_content = response.choices[0].message.content
return html_content.encode('utf-8')
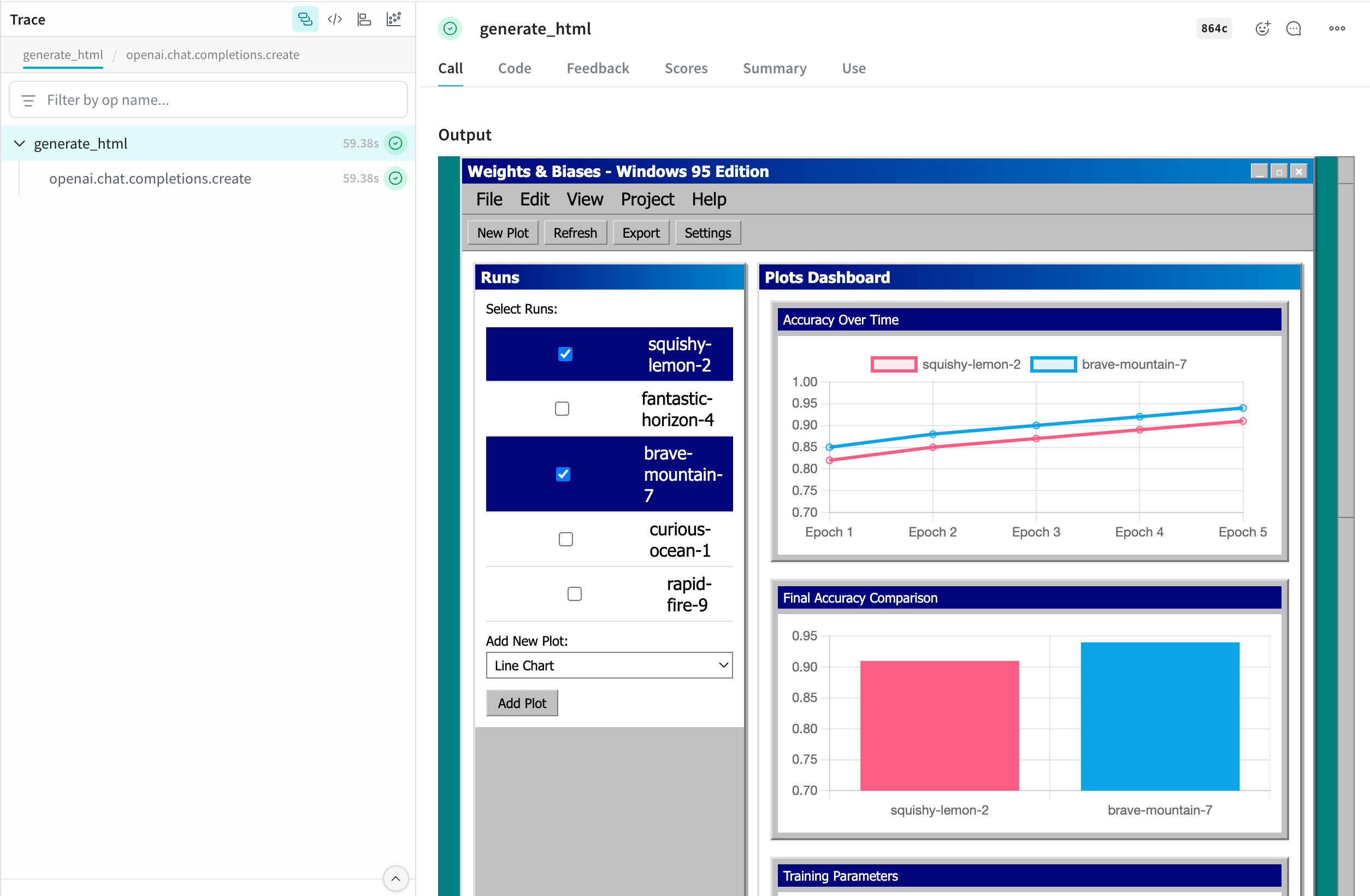
prompt = "Weights & Biases UI but with multi-run selection and plots, but it looks like Windows 95. Include 5 plots with comparisons of each run, bar plots, parallel coordinates and line plots for the runs. Use mock data for the runs. Make it possible to add new plots. Give the runs names like squishy-lemon-2, fantastic-horizon-4 etc. with random adjectives & nouns."
result = generate_html(prompt, prompt_template)
This HTML is logged to Weave and automatically displayed in the UI. Clicking the file_name.html cell in the table opens it in full screen. You can also download the raw .html file.
Using the Contents API
The Content API handles media objects in Weave. It allows you to import content into Weave as base64 data, file paths, raw bytes, or text.
The Content API is only available in Python.
Usage
There are two primary ways to use the Content API: type annotations and direct initialization.
Type annotations automatically detect the proper constructor to use, while direct initialization provides more fine-grained control and lets you take advantage of runtime features of the Content API in your code.
Type Annotations
The Weave Content API is designed to primarily be used through type annotations, which signal to Weave that traced inputs and outputs should be processed and stored as content blobs.
import weave
from weave import Content
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Annotated
@weave.op
def content_annotation(path: Annotated[str, Content]) -> Annotated[bytes, Content]:
data = Path(path).read_bytes()
return data
# Both input and output will show up as an MP4 file in Weave
# Input is a string and return value is bytes
bytes_data = content_annotation('./path/to/your/file.mp4')
Direct Initialization
If you want to take advantage of features, such as:
- Opening a file with a default application (such as a PDF viewer)
- Dumping the model to JSON to upload to your own blob storage (such as S3)
- Passing custom metadata to associate with the
Contentblob (such as the model used to generate it)
You can initialize content directly from your target type using one of the following methods:
Content.from_path- Create from a file pathContent.from_bytes- Create from raw bytesContent.from_text- Create from text stringContent.from_base64- Create from base64-encoded data
import weave
from weave import Content
@weave.op
def content_initialization(path: str) -> Content:
return Content.from_path(path)
# Input shows up as path string and output as PDF file in Weave
content = content_initialization('./path/to/your/file.pdf')
content.open() # Opens the file in your PDF viewer
content.model_dump() # Dumps the model attributes to JSON
Custom Mimetypes
Weave can detect most binary mimetypes, but custom mimetypes and text documents such as markdown may not be automatically detected, requiring you to manually specify the mimetype or extension of your file.
Custom Mimetypes with Type Annotations
import weave
from weave import Content
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Annotated, Literal
@weave.op
def markdown_content(
path: Annotated[str, Content[Literal['md']]]
) -> Annotated[str, Content[Literal['text/markdown']]]:
return Path(path).read_text()
markdown_content('path/to/your/document.md')
Custom Mimetypes with Direct Initialization
video_bytes = Path('/path/to/video.mp4').read_bytes()
# Pass an extension such as 'mp4' or '.mp4' to the extension parameter
# (not available for `from_path`)
content = Content.from_bytes(video_bytes, extension='.mp4')
# Pass a mimetype such as 'video/mp4' to the mimetype parameter
content = Content.from_bytes(video_bytes, mimetype='video/mp4')
Content properties
For a comprehensive list of class attributes and methods, view the Content reference docs
Attributes
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
data | bytes | Raw binary content |
metadata | dict[str, Any] | Custom metadata dictionary |
size | int | Size of content in bytes |
filename | str | Extracted or provided filename |
extension | str | File extension (e.g., "jpg", "mp3") |
mimetype | str | MIME type (e.g., "image/jpeg") |
path | str | None | Source file path, if applicable |
digest | str | SHA256 hash of the content |
Utility Methods
save(dest: str | Path) -> None: Save content to a fileopen() -> bool: Open file using system default application (requires the content to have been saved or loaded from a path)as_string() -> str: Display the data as a string (bytes are decoded using the encoding attribute)
Initialization Methods
Create content object from a file path:
content = Content.from_path("assets/photo.jpg")
print(content.mimetype, content.size)
Create content object from raw bytes:
content = Content.from_bytes(
data_bytes,
filename="audio.mp3",
mimetype="audio/mpeg"
)
content.save("output.mp3")
Create content object from text:
content = Content.from_text("Hello, World!", mimetype="text/plain")
print(content.as_string())
Create content object from base64-encoded data:
content = Content.from_base64(base64_string)
print(content.metadata)
Adding Custom Metadata
You can attach custom metadata to any Content object:
content = Content.from_bytes(
data,
metadata={"resolution": "1920x1080", "model": "dall-e-3" }
)
print(content.metadata["resolution"])