Google Agent Development Kit (ADK)
You can trace Google Agent Development Kit (ADK) agent and tool calls in Weave using OpenTelemetry (OTEL). ADK is a flexible and modular framework for developing and deploying AI agents. While optimized for Gemini and the Google ecosystem, ADK is model-agnostic and deployment-agnostic. It provides tools for creating, deploying, and orchestrating agentic architectures ranging from simple tasks to complex workflows.
This guide explains how to trace ADK agent and tool calls using OTEL, and visualize those traces in Weave. You'll learn how to install the required dependencies, configure an OTEL tracer to send data to Weave, and instrument your ADK agents and tools.
For more information on OTEL tracing in Weave, see Send OTEL Traces to Weave.
Prerequisites
-
Install the required dependencies:
pip install google-adk opentelemetry-sdk opentelemetry-exporter-otlp-proto-http -
Set your Google API key as an environment variable:
export GOOGLE_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
Configure OTEL tracing in Weave
To send traces from ADK to Weave, configure OTEL with a TracerProvider and an OTLPSpanExporter. Set the exporter to the correct endpoint and HTTP headers for authentication and project identification.
It is recommended that you store sensitive environment variables like your API key and project info in an environment file (e.g., .env), and load them using os.environ. This keeps your credentials secure and out of your codebase.
Required configuration
- Endpoint:
https://trace.wandb.ai/otel/v1/traces. If you are using a dedicated Weave instance, the URL follows this pattern instead:{YOUR_WEAVE_HOST}/traces/otel/v1/traces - Headers:
Authorization: Basic auth using your W&B API keyproject_id: Your W&B entity/project name (e.g.,myteam/myproject)
Send OTEL traces from ADK to Weave
The following code snippet demonstrates how to configure an OTLP span exporter and tracer provider to send OTEL traces from an ADK application to Weave.
To ensure that Weave traces ADK properly, set the global tracer provider before using ADK components in your code.
import base64
import os
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http.trace_exporter import OTLPSpanExporter
from opentelemetry.sdk import trace as trace_sdk
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace.export import SimpleSpanProcessor
from opentelemetry import trace
# Load sensitive values from environment variables
WANDB_BASE_URL = "https://trace.wandb.ai"
# Your W&B entity/project name e.g. "myteam/myproject"
PROJECT_ID = os.environ.get("WANDB_PROJECT_ID")
# Your W&B API key (found at https://wandb.ai/authorize)
WANDB_API_KEY = os.environ.get("WANDB_API_KEY")
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT = f"{WANDB_BASE_URL}/otel/v1/traces"
AUTH = base64.b64encode(f"api:{WANDB_API_KEY}".encode()).decode()
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS = {
"Authorization": f"Basic {AUTH}",
"project_id": PROJECT_ID,
}
# Create the OTLP span exporter with endpoint and headers
exporter = OTLPSpanExporter(
endpoint=OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT,
headers=OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS,
)
# Create a tracer provider and add the exporter
tracer_provider = trace_sdk.TracerProvider()
tracer_provider.add_span_processor(SimpleSpanProcessor(exporter))
# Set the global tracer provider BEFORE importing/using ADK
trace.set_tracer_provider(tracer_provider)
Trace ADK Agents with OTEL
After setting up the tracer provider, you can create and run ADK agents with automatic tracing. The following example demonstrates how to create a simple LLM agent with a tool, and run it with an in-memory runner:
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
from google.adk.runners import InMemoryRunner
from google.adk.tools import FunctionTool
from google.genai import types
import asyncio
# Define a simple tool for demonstration
def calculator(a: float, b: float) -> str:
"""Add two numbers and return the result.
Args:
a: First number
b: Second number
Returns:
The sum of a and b
"""
return str(a + b)
calculator_tool = FunctionTool(func=calculator)
async def run_agent():
# Create an LLM agent
agent = LlmAgent(
name="MathAgent",
model="gemini-2.0-flash", # You can change this to another model if needed
instruction=(
"You are a helpful assistant that can do math. "
"When asked a math problem, use the calculator tool to solve it."
),
tools=[calculator_tool],
)
# Set up runner
runner = InMemoryRunner(agent=agent, app_name="math_assistant")
session_service = runner.session_service
# Create a session
user_id = "example_user"
session_id = "example_session"
await session_service.create_session(
app_name="math_assistant",
user_id=user_id,
session_id=session_id,
)
# Run the agent with a message that should trigger tool use
async for event in runner.run_async(
user_id=user_id,
session_id=session_id,
new_message=types.Content(
role="user", parts=[types.Part(text="What is 5 + 7?")]
),
):
if event.is_final_response() and event.content:
print(f"Final response: {event.content.parts[0].text.strip()}")
# Run the async function
asyncio.run(run_agent())
All agent operations are automatically traced and sent to Weave, allowing you to visualize the execution flow. You can view model calls, reasoning steps, and tool invocations.
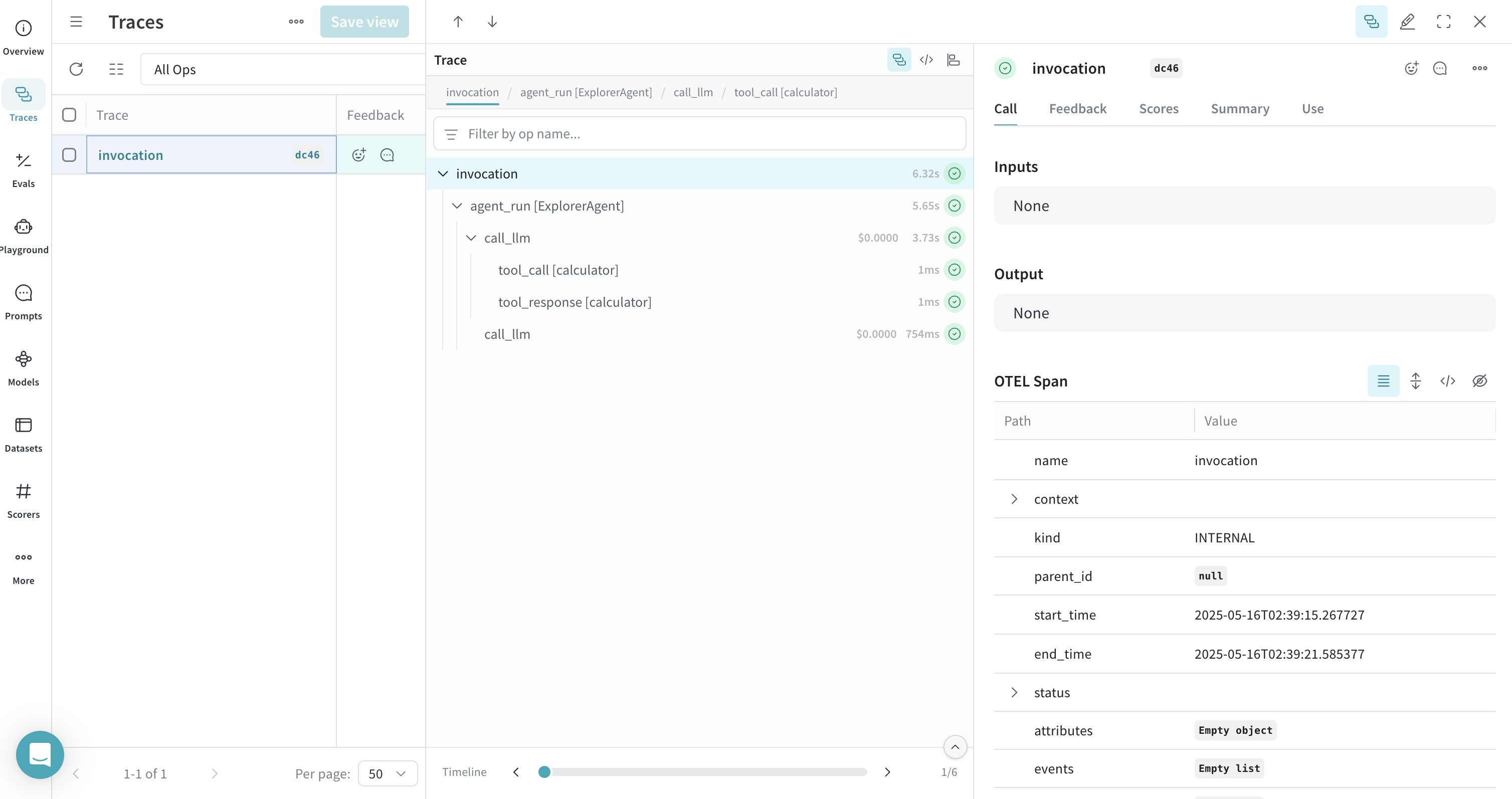
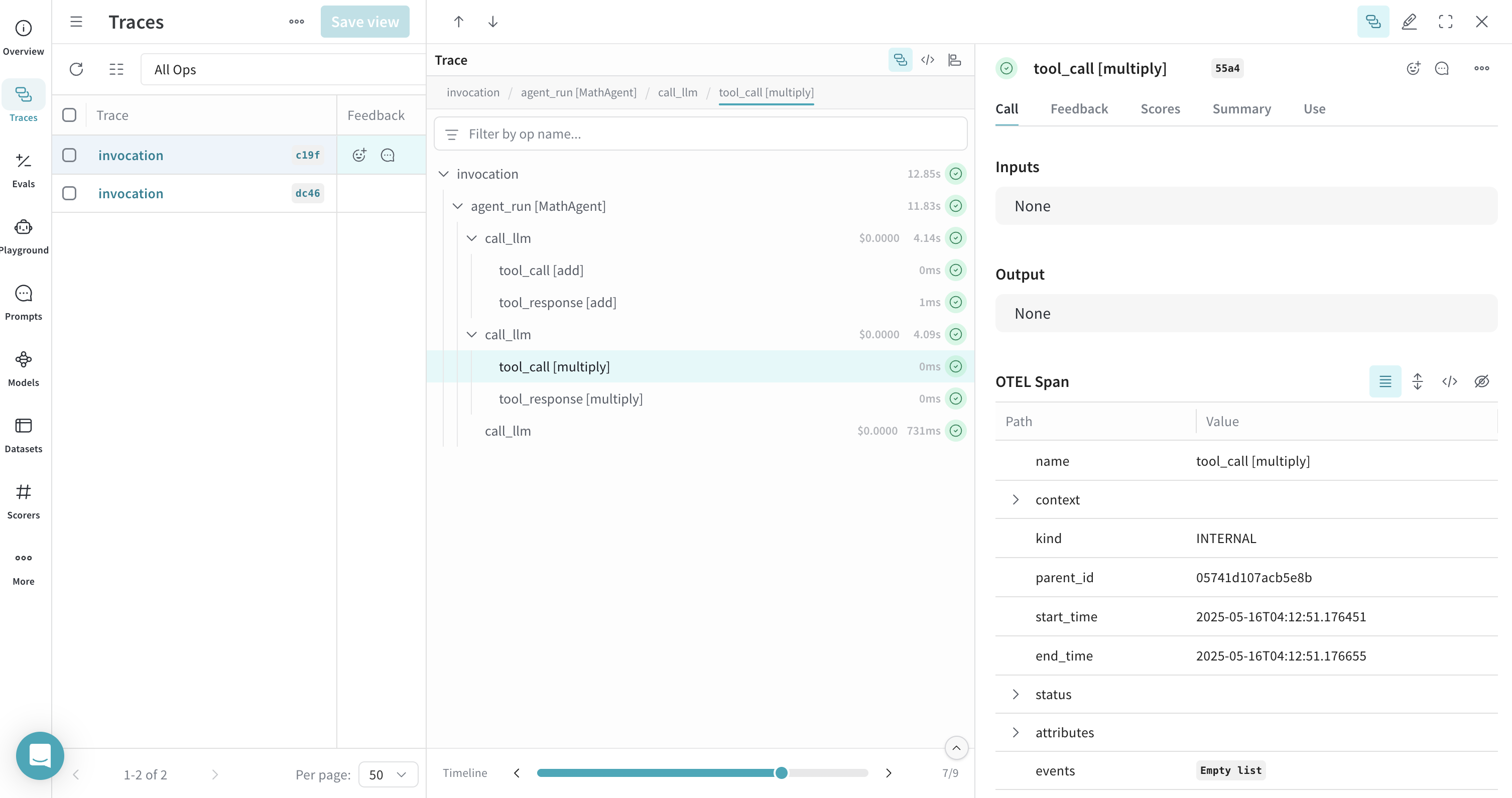
Trace ADK Tools with OTEL
When you define and use tools with ADK, these tool calls are also captured in the trace. The OTEL integration automatically instruments both the agent's reasoning process and the individual tool executions, providing a comprehensive view of your agent's behavior.
Here's an example with multiple tools:
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
from google.adk.runners import InMemoryRunner
from google.adk.tools import FunctionTool
from google.genai import types
import asyncio
# Define multiple tools
def add(a: float, b: float) -> str:
"""Add two numbers.
Args:
a: First number
b: Second number
Returns:
The sum of a and b
"""
return str(a + b)
def multiply(a: float, b: float) -> str:
"""Multiply two numbers.
Args:
a: First number
b: Second number
Returns:
The product of a and b
"""
return str(a * b)
# Create function tools
add_tool = FunctionTool(func=add)
multiply_tool = FunctionTool(func=multiply)
async def run_agent():
# Create an LLM agent with multiple tools
agent = LlmAgent(
name="MathAgent",
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
instruction=(
"You are a helpful assistant that can do math operations. "
"When asked to add numbers, use the add tool. "
"When asked to multiply numbers, use the multiply tool."
),
tools=[add_tool, multiply_tool],
)
# Set up runner
runner = InMemoryRunner(agent=agent, app_name="math_assistant")
session_service = runner.session_service
# Create a session
user_id = "example_user"
session_id = "example_session"
await session_service.create_session(
app_name="math_assistant",
user_id=user_id,
session_id=session_id,
)
# Run the agent with a message that should trigger tool use
async for event in runner.run_async(
user_id=user_id,
session_id=session_id,
new_message=types.Content(
role="user", parts=[types.Part(text="First add 5 and 7, then multiply the result by 2.")]
),
):
if event.is_final_response() and event.content:
print(f"Final response: {event.content.parts[0].text.strip()}")
# Run the async function
asyncio.run(run_agent())
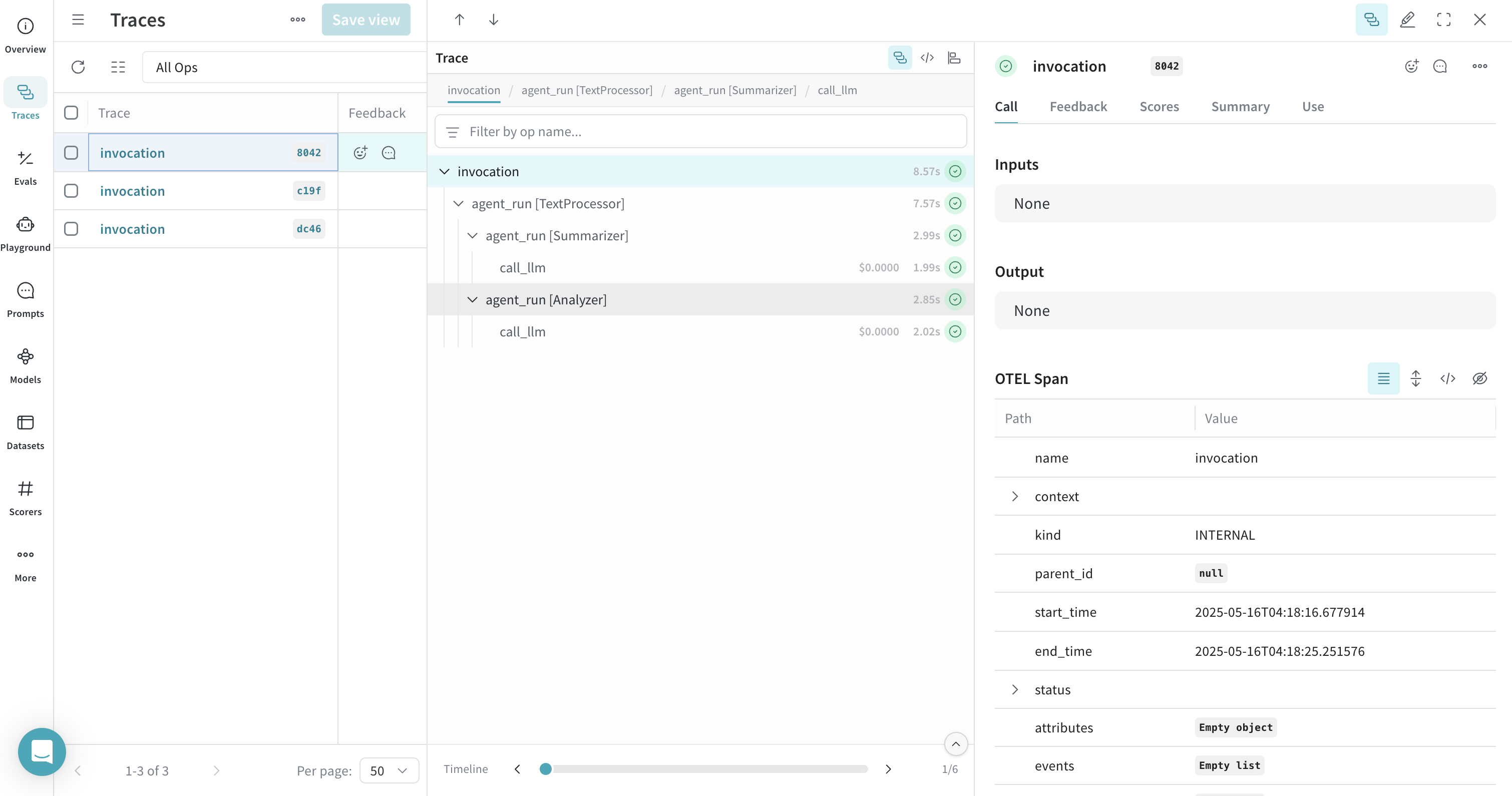
Work with Workflow Agents
ADK provides various workflow agents for more complex scenarios. You can trace workflow agents just like regular LLM agents. Here's an example using a SequentialAgent:
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent, SequentialAgent
from google.adk.runners import InMemoryRunner
from google.genai import types
import asyncio
async def run_workflow():
# Create two LLM agents
summarizer = LlmAgent(
name="Summarizer",
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
instruction="Summarize the given text in one sentence.",
description="Summarizes text in one sentence",
output_key="summary" # Store output in state['summary']
)
analyzer = LlmAgent(
name="Analyzer",
model="gemini-2.0-flash",
instruction="Analyze the sentiment of the given text as positive, negative, or neutral. The text to analyze: {summary}",
description="Analyzes sentiment of text",
output_key="sentiment" # Store output in state['sentiment']
)
# Create a sequential workflow
workflow = SequentialAgent(
name="TextProcessor",
sub_agents=[summarizer, analyzer],
description="Executes a sequence of summarization followed by sentiment analysis.",
)
# Set up runner
runner = InMemoryRunner(agent=workflow, app_name="text_processor")
session_service = runner.session_service
# Create a session
user_id = "example_user"
session_id = "example_session"
await session_service.create_session(
app_name="text_processor",
user_id=user_id,
session_id=session_id,
)
# Run the workflow
async for event in runner.run_async(
user_id=user_id,
session_id=session_id,
new_message=types.Content(
role="user",
parts=[types.Part(text="The product exceeded my expectations. It worked perfectly right out of the box, and the customer service was excellent when I had questions about setup.")]
),
):
if event.is_final_response() and event.content:
print(f"Final response: {event.content.parts[0].text.strip()}")
# Run the async function
asyncio.run(run_workflow())
This workflow agent trace will show the sequential execution of both agents in Weave, providing visibility into how data flows through your multi-agent system.