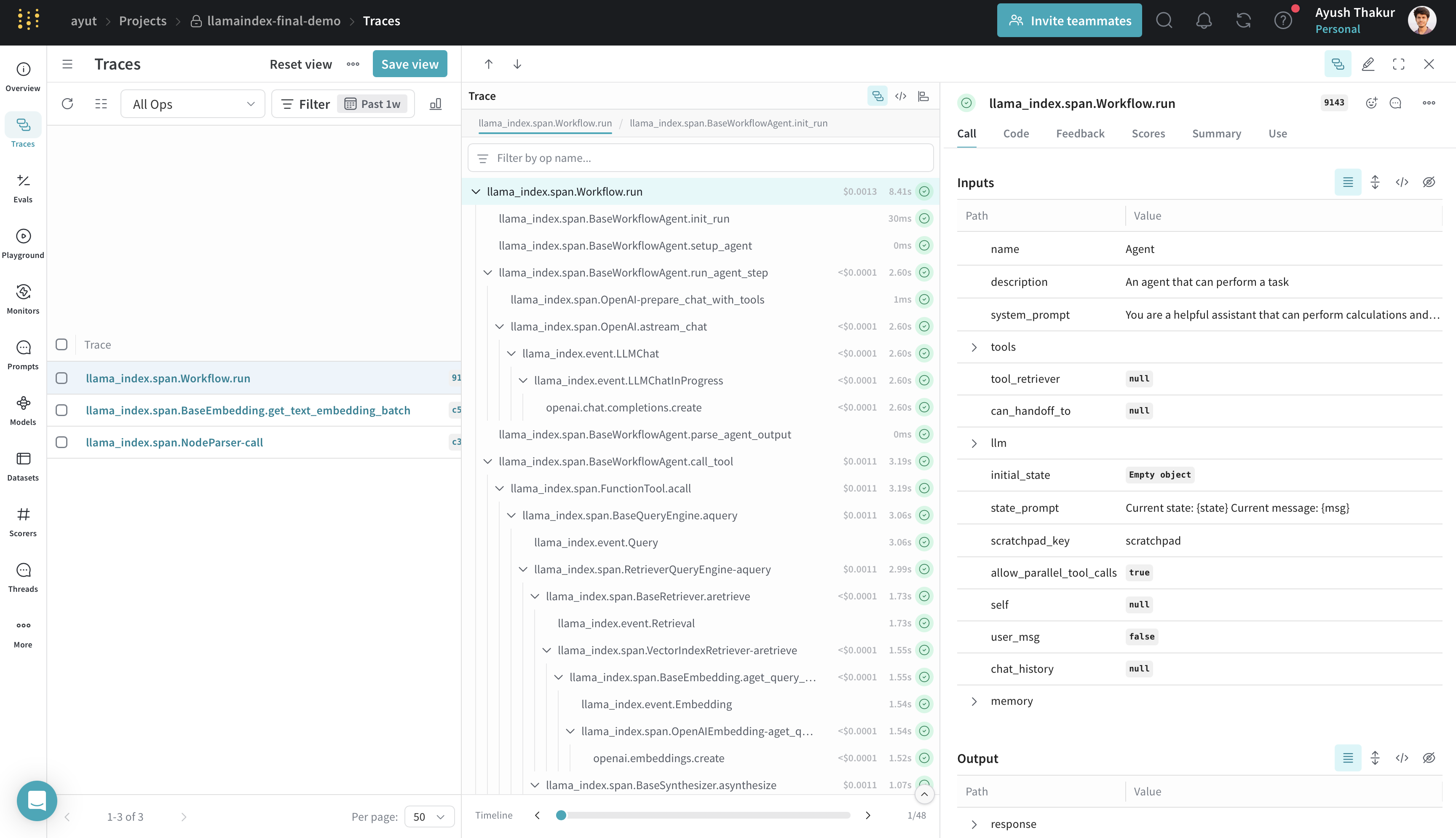
LlamaIndex
Weave integrates with LlamaIndex, a powerful framework for building LLM-driven applications like RAG systems, chatbots, and agents.
Using LlamaIndex’s instrumentation system, the Weave integration automatically captures:
- Execution time: Duration of each operation
- Token usage: Input and output token counts
- Cost tracking: Estimated costs for API calls
- Inputs and outputs: Full request and response data
- Error handling: Detailed error traces and stack traces
- Nested operations: Complete trace hierarchy showing parent-child relationships
- Streaming data: Accumulated streaming responses
All trace data is viewable in the Weave UI, making it easy to debug and optimize your LlamaIndex applications.
For a basic usage example, see Get started. For more examples demonstrating advanced usage, see Advanced usage and the Complete example: Tracking agents.
Get started
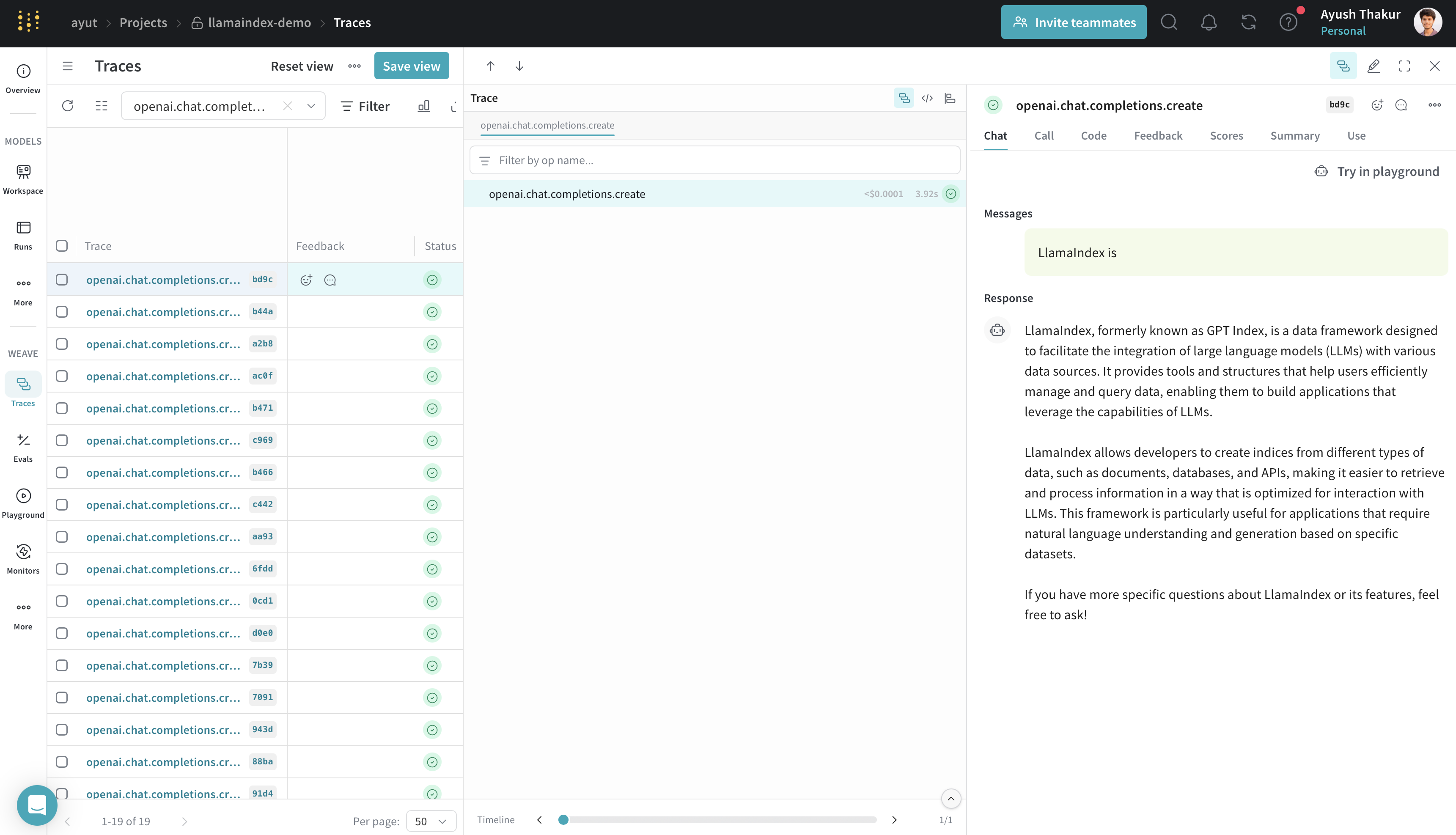
To get started, call weave.init() in your LLM application. The integration will begin tracing all LlamaIndex operations automatically.
The example below initializes a Weave project llamaindex-demo, sends a prompt to gpt-4o-mini, and prints the result.
import weave
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
# Initialize Weave with your project name
weave.init("llamaindex-demo")
# All LlamaIndex operations are now automatically traced
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
response = llm.complete("William Shakespeare is ")
print(response)
Next, try out the examples in Advanced usage.
Advanced usage
The examples below demonstrate more advanced LlamaIndex features, including streaming, chat, tool calling, and workflows. Each example includes a short description of what it does and how Weave traces it.
Synchronous and asynchronous completions
Use these methods to get text completions either synchronously or with await. Weave traces both methods.
import weave
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
weave.init("llamaindex-demo")
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
# Synchronous completion
response = llm.complete("William Shakespeare is ")
print(response)
# Asynchronous completion
response = await llm.acomplete("William Shakespeare is ")
print(response)
Streaming operations
LlamaIndex supports streaming token output from completions. Weave captures the token stream for both sync and async modes.
import weave
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
weave.init("llamaindex-demo")
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
# Synchronous streaming
handle = llm.stream_complete("William Shakespeare is ")
for token in handle:
print(token.delta, end="", flush=True)
# Asynchronous streaming
handle = await llm.astream_complete("William Shakespeare is ")
async for token in handle:
print(token.delta, end="", flush=True)
Chat interface
The chat interface allows for back-and-forth message exchanges. This is useful for building assistants or more interactive experiences. Weave traces all chat interactions.
import weave
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
from llama_index.core.llms import ChatMessage
weave.init("llamaindex-demo")
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
messages = [
ChatMessage(role="system", content="You are a helpful assistant."),
ChatMessage(role="user", content="Tell me a joke."),
]
# Synchronous chat
response = llm.chat(messages)
print(response)
# Asynchronous chat
response = await llm.achat(messages)
print(response)
# Streaming chat
handle = llm.stream_chat(messages)
for token in handle:
print(token.delta, end="", flush=True)
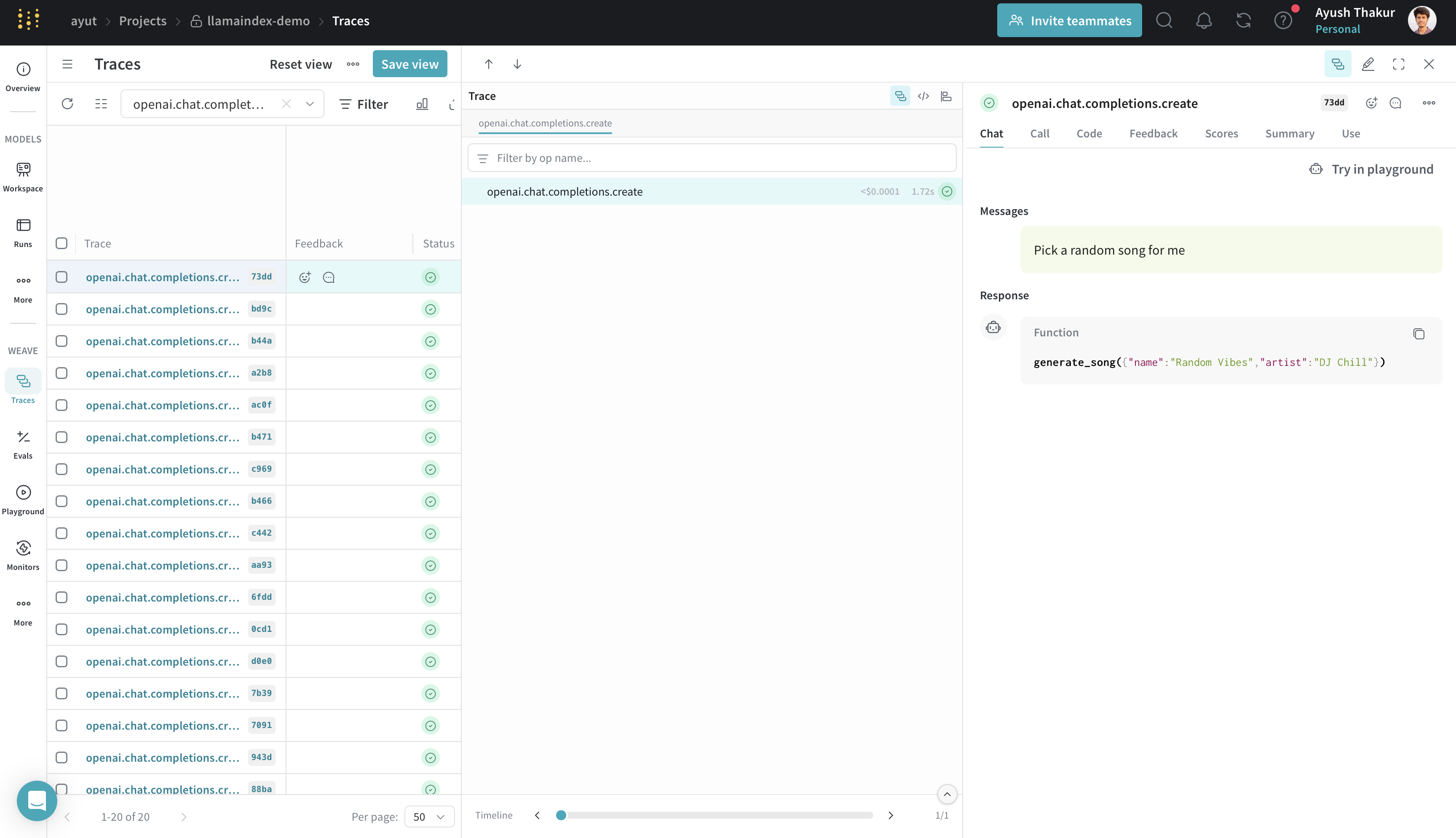
Tool calling
Tool calling is commonly used when building agents and workflows. Weave automatically traces each tool call and its result.
import weave
from pydantic import BaseModel
from llama_index.core.tools import FunctionTool
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
weave.init("llamaindex-demo")
class Song(BaseModel):
name: str
artist: str
def generate_song(name: str, artist: str) -> Song:
return Song(name=name, artist=artist)
tool = FunctionTool.from_defaults(fn=generate_song)
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
response = llm.predict_and_call([tool], "Pick a random song for me")
print(response)
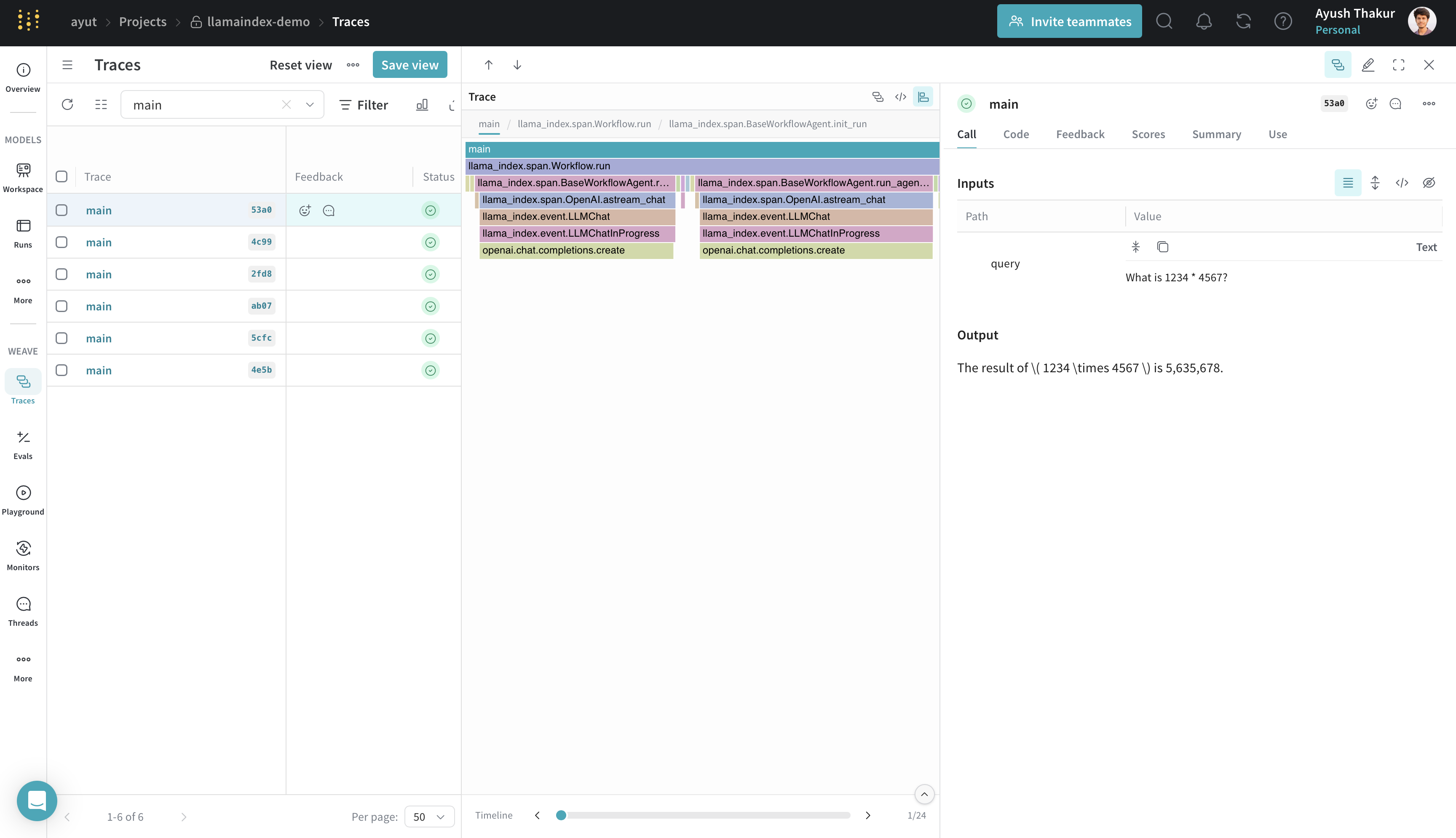
Tracking agents
Agents in LlamaIndex use LLMs and tools to solve tasks. They can ask clarifying questions or call functions repeatedly. Weave captures every step in the flow.
import asyncio
import weave
from llama_index.core.agent.workflow import FunctionAgent
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
from llama_index.core.memory import ChatMemoryBuffer
weave.init("llamaindex-demo")
def multiply(a: float, b: float) -> float:
return a * b
agent = FunctionAgent(
tools=[multiply],
llm=OpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini"),
system_prompt="You are a helpful assistant that can multiply two numbers.",
)
memory = ChatMemoryBuffer.from_defaults(token_limit=40000)
@weave.op()
async def main(query: str):
response = await agent.run(query, memory=memory)
return str(response)
if __name__ == "__main__":
response = asyncio.run(main("What is 1234 * 4567?"))
print(response)
The @weave.op() decorator wraps the main() function so it can be traced in Weave. This helps capture custom async workflows clearly in the trace tree.
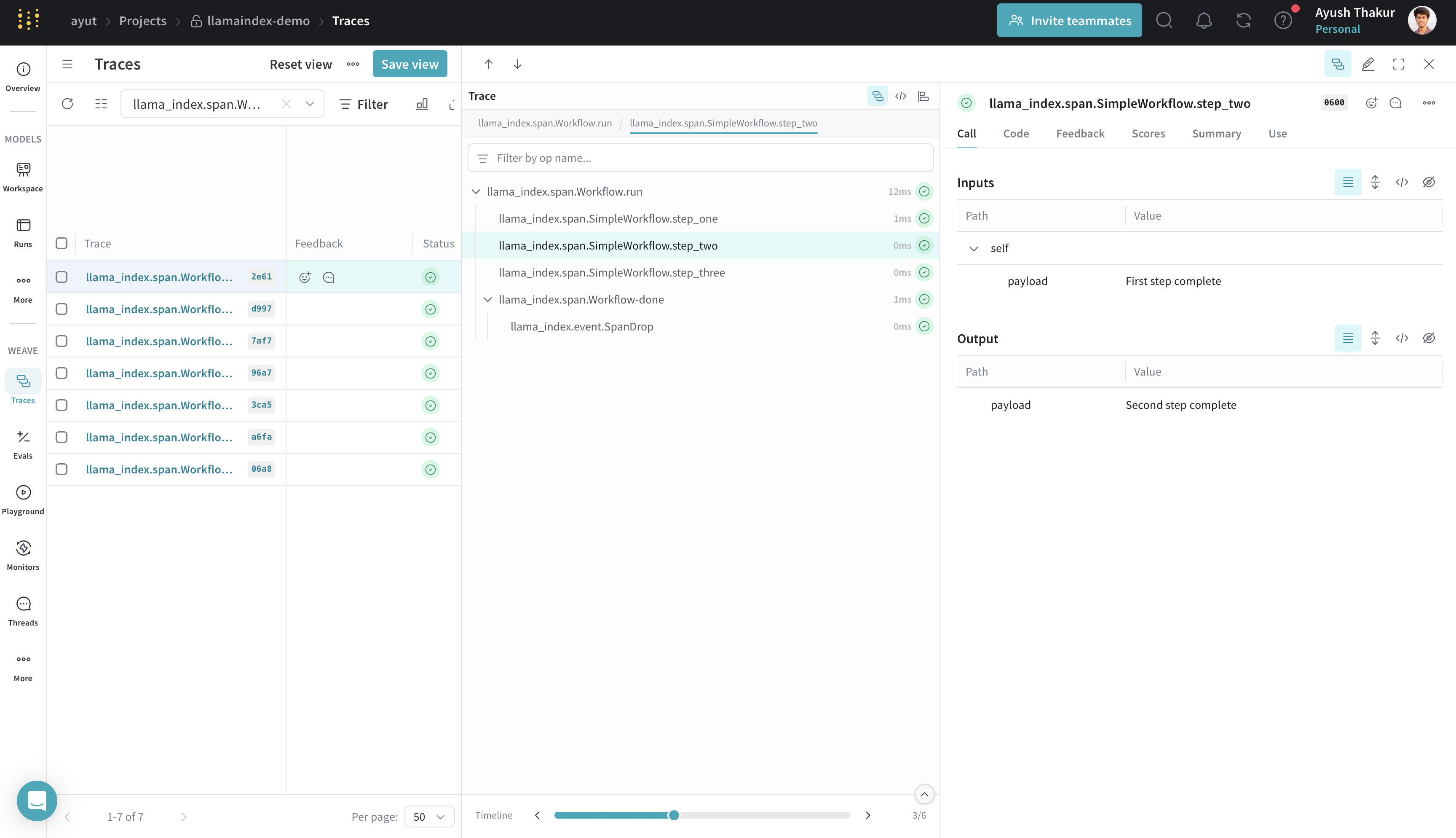
Workflows
LlamaIndex workflows use event-based steps to build structured execution logic. Weave traces each step and the data passed between them.
import weave
from llama_index.core.workflow import (
StartEvent,
StopEvent,
Workflow,
step,
Event,
)
weave.init("llamaindex-demo")
class FirstEvent(Event):
payload: str
class SecondEvent(Event):
payload: str
class SimpleWorkflow(Workflow):
@step
async def step_one(self, ev: StartEvent) -> FirstEvent:
return FirstEvent(payload="First step complete")
@step
async def step_two(self, ev: FirstEvent) -> SecondEvent:
return SecondEvent(payload="Second step complete")
@step
async def step_three(self, ev: SecondEvent) -> StopEvent:
return StopEvent(result="Workflow complete")
workflow = SimpleWorkflow(timeout=10, verbose=False)
result = await workflow.run(first_input="Start the workflow")
print(result)
Weave traces each event and transition, which is useful for debugging multi-step flows with conditionals, branches, or loops.
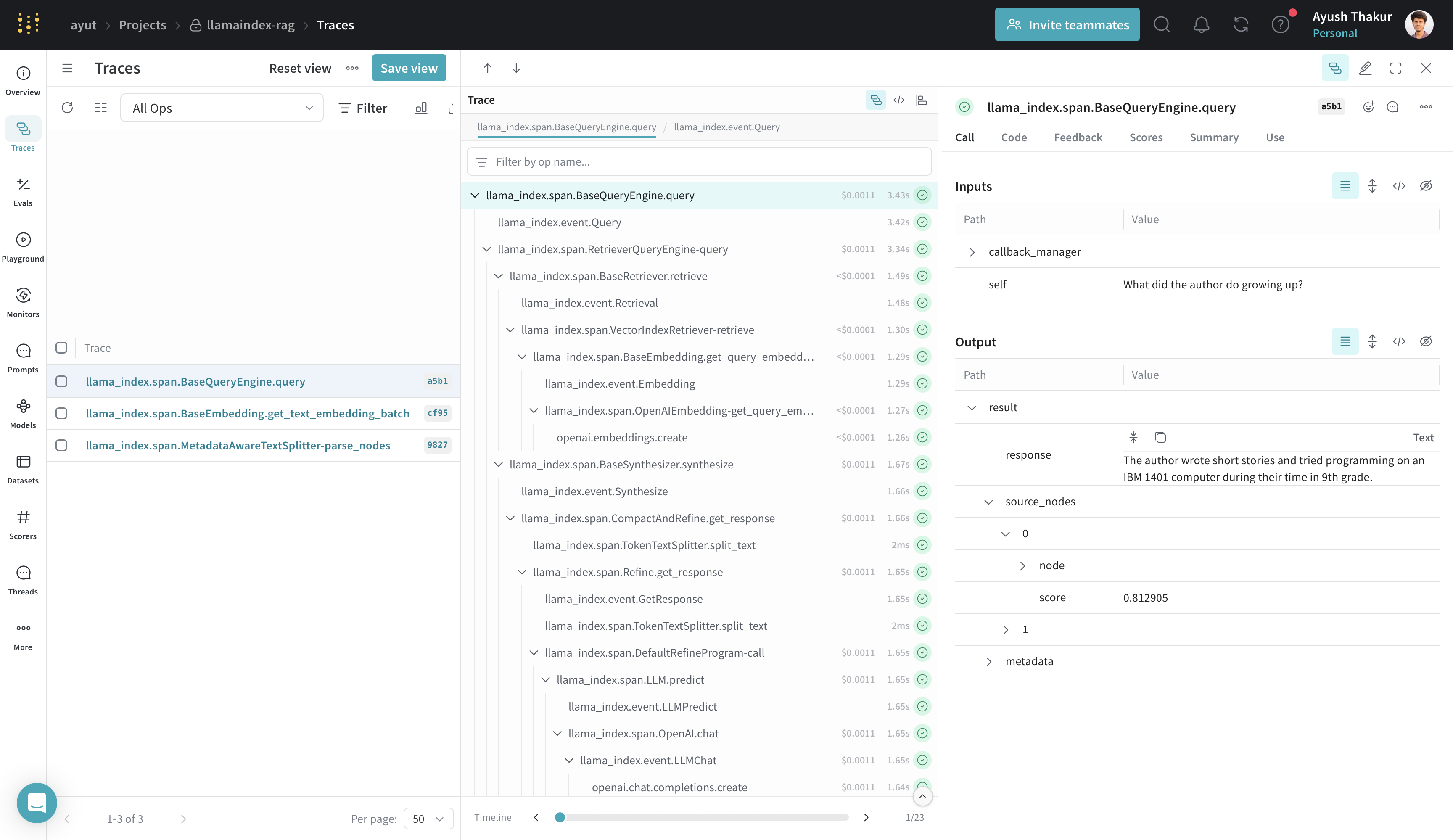
RAG pipelines
RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) pipelines use LLMs with external context. This example loads documents, builds an index, and queries it. Weave traces the parsing, indexing, and querying stages.
import weave
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
weave.init("llamaindex-demo")
# Load and process documents
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("data").load_data()
parser = SentenceSplitter()
nodes = parser.get_nodes_from_documents(documents)
# Create index and query engine
index = VectorStoreIndex(nodes)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
# Query the documents
response = query_engine.query("What did the author do growing up?")
print(response)
Weave shows separate traces for node parsing, index creation, and querying. To view all steps under a single trace, wrap the logic in a @weave.op() function. Note that parsing and indexing are typically one-time setup steps.
Complete example: Tracking agents
This end-to-end example shows how to combine a document search tool and a math tool in a single agent. Weave traces the full interaction, including tool calls and the final response.
import weave
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader
from llama_index.core.agent.workflow import FunctionAgent
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
weave.init("llamaindex-demo")
# Create a RAG tool
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("data").load_data()
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
def multiply(a: float, b: float) -> float:
return a * b
async def search_documents(query: str) -> str:
response = await query_engine.aquery(query)
return str(response)
# Create an agent with both tools
agent = FunctionAgent(
tools=[multiply, search_documents],
llm=OpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini"),
system_prompt="""You are a helpful assistant that can perform calculations
and search through documents to answer questions.""",
)
response = await agent.run(
"What did the author do in college? Also, what's 7 * 8?"
)
print(response)
This combines retrieval and arithmetic tasks. Weave traces the question routing, tool invocations, and agent response timeline.