NVIDIA NIM
Weave automatically tracks and logs LLM calls made via the ChatNVIDIA library, after weave.init() is called.
For the latest tutorials, visit Weights & Biases on NVIDIA.
Tracing
It’s important to store traces of LLM applications in a central database, both during development and in production. You’ll use these traces for debugging and to help build a dataset of tricky examples to evaluate against while improving your application.
- Python
- TypeScript
Weave can automatically capture traces for the ChatNVIDIA python library.
Start capturing by calling weave.init(<project-name>) with a project name of your choice. If you don't specify a W&B team when you call `weave.init()`, your default entity is used. To find or update your default entity, refer to [User Settings](https://docs.wandb.ai/guides/models/app/settings-page/user-settings/#default-team) in the W&B Models documentation.
from langchain_nvidia_ai_endpoints import ChatNVIDIA
import weave
client = ChatNVIDIA(model="mistralai/mixtral-8x7b-instruct-v0.1", temperature=0.8, max_tokens=64, top_p=1)
weave.init('emoji-bot')
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are AGI. You will be provided with a message, and your task is to respond using emojis only."
}]
response = client.invoke(messages)
This feature is not available in TypeScript yet since this library is only in Python.
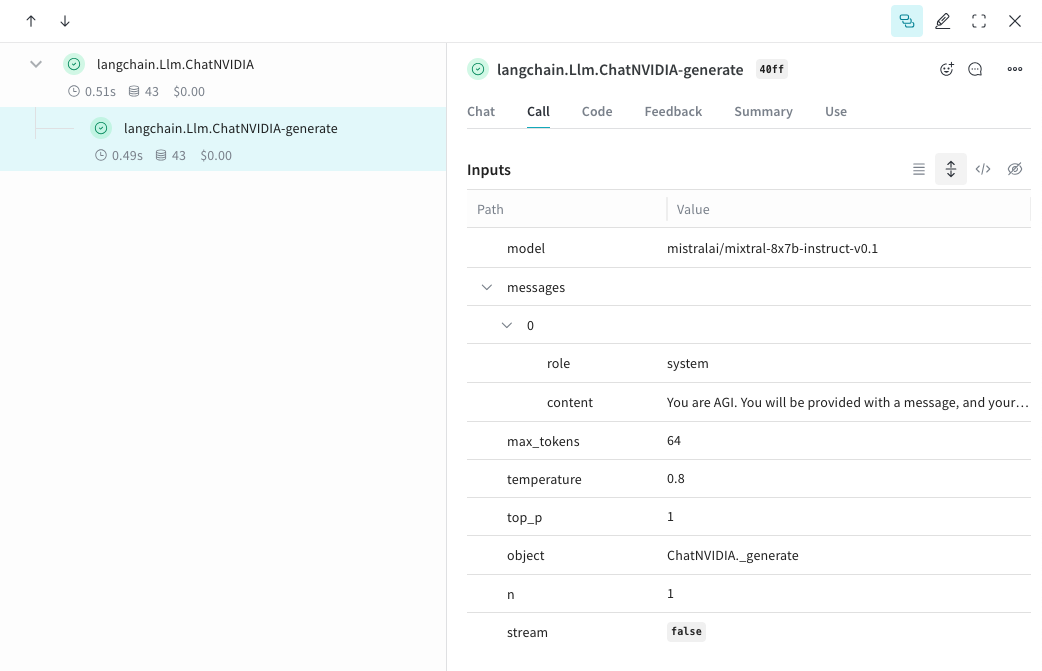
Track your own ops
- Python
- TypeScript
Wrapping a function with @weave.op starts capturing inputs, outputs and app logic so you can debug how data flows through your app. You can deeply nest ops and build a tree of functions that you want to track. This also starts automatically versioning code as you experiment to capture ad-hoc details that haven't been committed to git.
Simply create a function decorated with @weave.op that calls into ChatNVIDIA python library.
In the example below, we have 2 functions wrapped with op. This helps us see how intermediate steps, like the retrieval step in a RAG app, are affecting how our app behaves.
import weave
from langchain_nvidia_ai_endpoints import ChatNVIDIA
import requests, random
PROMPT="""Emulate the Pokedex from early Pokémon episodes. State the name of the Pokemon and then describe it.
Your tone is informative yet sassy, blending factual details with a touch of dry humor. Be concise, no more than 3 sentences. """
POKEMON = ['pikachu', 'charmander', 'squirtle', 'bulbasaur', 'jigglypuff', 'meowth', 'eevee']
client = ChatNVIDIA(model="mistralai/mixtral-8x7b-instruct-v0.1", temperature=0.7, max_tokens=100, top_p=1)
@weave.op
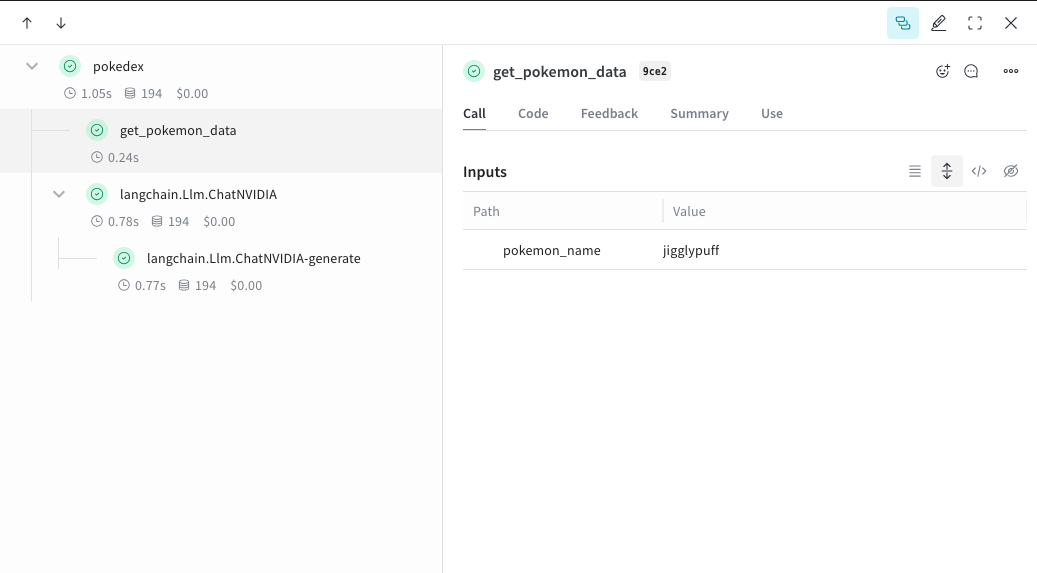
def get_pokemon_data(pokemon_name):
# This is a step within your application, like the retrieval step within a RAG app
url = f"https://pokeapi.co/api/v2/pokemon/{pokemon_name}"
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
name = data["name"]
types = [t["type"]["name"] for t in data["types"]]
species_url = data["species"]["url"]
species_response = requests.get(species_url)
evolved_from = "Unknown"
if species_response.status_code == 200:
species_data = species_response.json()
if species_data["evolves_from_species"]:
evolved_from = species_data["evolves_from_species"]["name"]
return {"name": name, "types": types, "evolved_from": evolved_from}
else:
return None
@weave.op
def pokedex(name: str, prompt: str) -> str:
# This is your root op that calls out to other ops
data = get_pokemon_data(name)
if not data: return "Error: Unable to fetch data"
messages=[
{"role": "system","content": prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": str(data)}
]
response = client.invoke(messages)
return response.content
weave.init('pokedex-nvidia')
# Get data for a specific Pokémon
pokemon_data = pokedex(random.choice(POKEMON), PROMPT)
Navigate to Weave and you can click get_pokemon_data in the UI to see the inputs & outputs of that step.
This feature is not available in TypeScript yet since this library is only in Python.
Create a Model for easier experimentation
- Python
- TypeScript
Organizing experimentation is difficult when there are many moving pieces. By using the Model class, you can capture and organize the experimental details of your app like your system prompt or the model you're using. This helps organize and compare different iterations of your app.
In addition to versioning code and capturing inputs/outputs, Models capture structured parameters that control your application’s behavior, making it easy to find what parameters worked best. You can also use Weave Models with serve, and Evaluations.
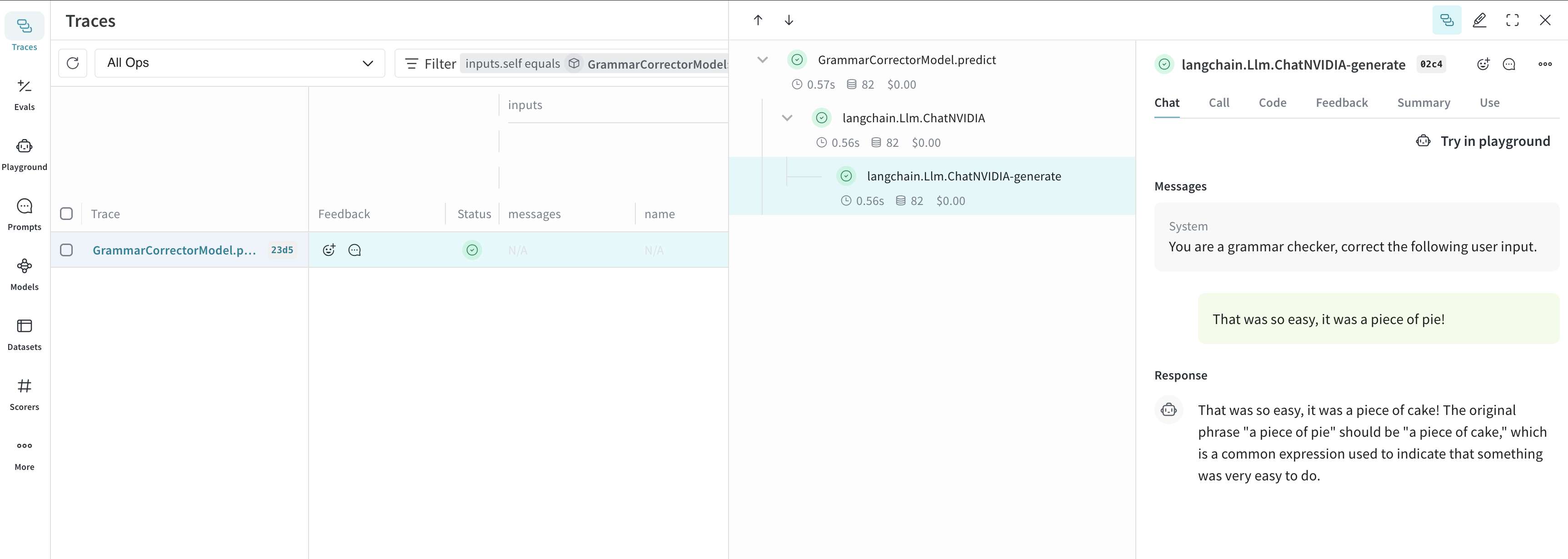
In the example below, you can experiment with model and system_message. Every time you change one of these, you'll get a new version of GrammarCorrectorModel.
import weave
from langchain_nvidia_ai_endpoints import ChatNVIDIA
weave.init('grammar-nvidia')
class GrammarCorrectorModel(weave.Model): # Change to `weave.Model`
system_message: str
@weave.op()
def predict(self, user_input): # Change to `predict`
client = ChatNVIDIA(model="mistralai/mixtral-8x7b-instruct-v0.1", temperature=0, max_tokens=100, top_p=1)
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": self.system_message
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": user_input
}
]
response = client.invoke(messages)
return response.content
corrector = GrammarCorrectorModel(
system_message = "You are a grammar checker, correct the following user input.")
result = corrector.predict("That was so easy, it was a piece of pie!")
print(result)
This feature is not available in TypeScript yet since this library is only in Python.
Usage Info
The ChatNVIDIA integration supports invoke, stream and their async variants. It also supports tool use.
As ChatNVIDIA is meant to be used with many types of models, it does not have function calling support.