Koog
Koog is a Kotlin-based framework for building single-run and complex workflow agents. Koog includes built-in OpenTelemetry (OTEL) support and can export traces directly to Weave, giving you rich visibility into prompts, completions, tool calls, and end-to-end agent execution.
With the Weave exporter enabled, Koog forwards OpenTelemetry spans to your Weave project so you can debug, analyze performance, and iterate faster.
Prerequisites
Set the following environment variables before running your agent:
export WEAVE_API_KEY="<your-api-key>"
export WEAVE_ENTITY="<your-entity>" # your W&B team/entity
export WEAVE_PROJECT_NAME="koog-tracing" # any project name; created on first use
Install Koog (Gradle)
Add Koog to your Kotlin project (Kotlin DSL shown):
dependencies {
implementation("ai.koog:koog-agents:LATEST_VERSION")
}
See Koog's documentation for additional installation information.
Enable Weave export (OpenTelemetry)
Install Koog’s OpenTelemetry feature and add the Weave exporter. This maps Koog spans to Weave traces using Weave’s OpenTelemetry endpoint.
The following example shows how to use the addWeaveExporter:
fun main() = runBlocking {
val apiKey = "api-key"
val entity = System.getenv()["WEAVE_ENTITY"] ?: throw IllegalArgumentException("WEAVE_ENTITY is not set")
val projectName = System.getenv()["WEAVE_PROJECT_NAME"] ?: "koog-tracing"
val agent = AIAgent(
executor = simpleOpenAIExecutor(apiKey),
llmModel = OpenAIModels.CostOptimized.GPT4oMini,
systemPrompt = "You are a code assistant. Provide concise code examples."
) {
install(OpenTelemetry) {
addWeaveExporter()
}
}
println("Running agent with Weave tracing")
val result = agent.run("""
Create a Python function to calculate fibonacci numbers efficiently,
include error handling, type hints, and unit tests.
Verify the implementation works for n=50.
""")
println("Result: $result\nSee traces on https://wandb.ai/$entity/$projectName/weave/traces")
}
The function automatically reads your Weave environment variables, but you can also configure specific parameters for the exporter, like this:
install(OpenTelemetry) {
addWeaveExporter(
weaveOtelBaseUrl = "https://trace.wandb.ai",
weaveEntity = System.getenv()["WEAVE_ENTITY"],
weaveProjectName = System.getenv()["WEAVE_PROJECT_NAME"],
weaveApiKey = System.getenv()["WEAVE_API_KEY"],
timeout = 10.seconds
)
}
The example above:
- Uses
weaveEntityandweaveProjectNameto route traces to a specific team and project. - Sets
weaveOtelBaseUrlto your trace endpoint (for example,https://<your-subdomain>.wandb.io/<path>). Use the parameter for dedicated Weave instances.
If you’re new to using Koog with Weave, we recommend reviewing the following pieces of documentation:
- Koog's Weave exporter guide for additional information about the exporter
- Koog's OpenTelemetry support guide for core concepts about how OpenTelemetry works with Koog
- Weave OTEL docs for information about how Weave ingests OTLP data
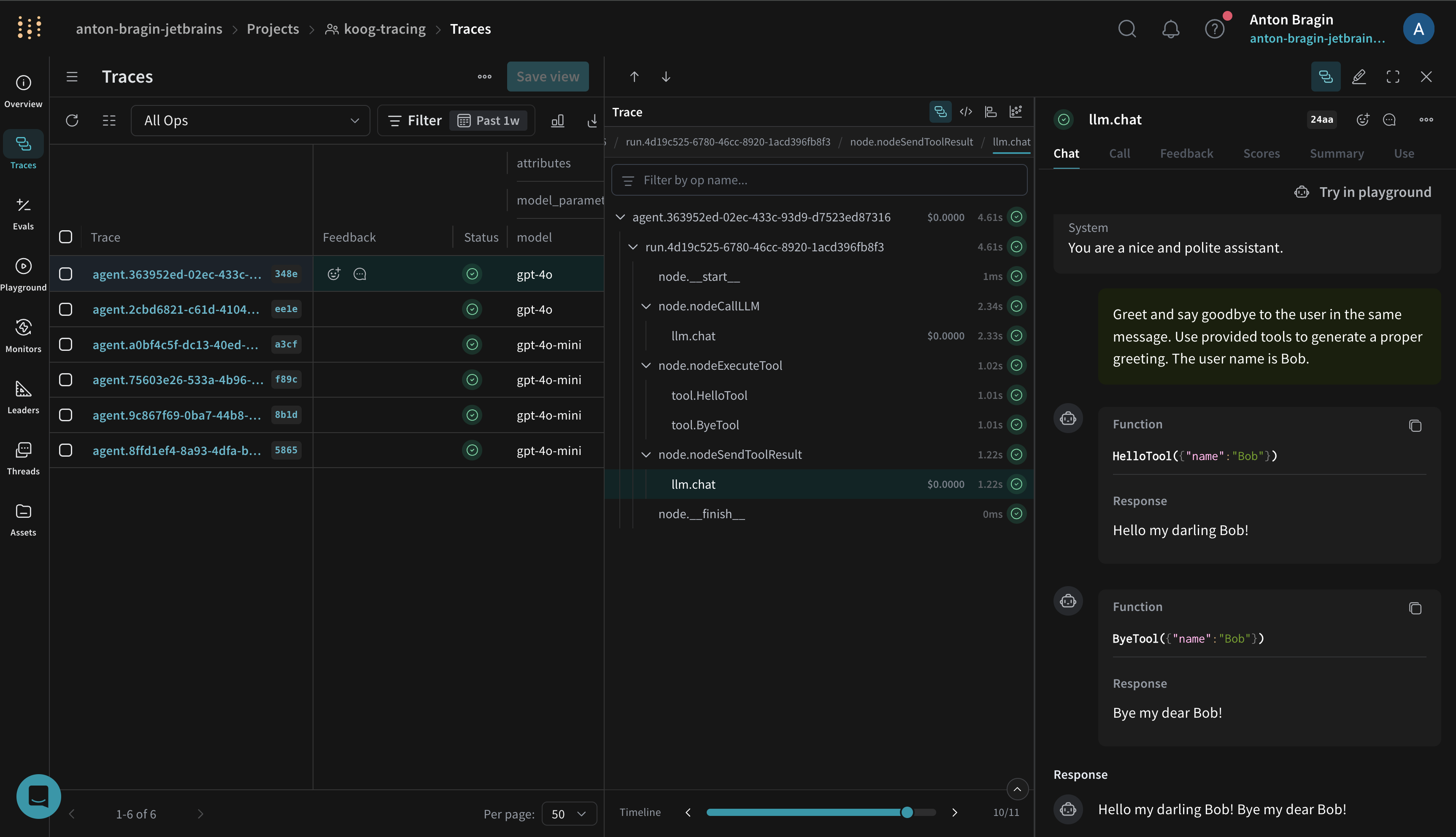
What gets traced
When enabled, Koog’s Weave exporter captures the same spans as Koog’s general OTEL integration, including:
- Agent lifecycle events (start, stop, errors)
- LLM interactions (prompts, completions, token usage, latency)
- Tool and API calls (function calls and external requests)
- System context (model name, Koog version, environment metadata)
You can visualize these traces in the Weave UI to understand performance and quality. See Weave's tracing overview for an introduction to capturing traces with Weave.
Example notebook
See Koog's documentation for a runnable notebooks that streams traces to Weave.
Troubleshooting
- If traces are missing, first verify that
WEAVE_API_KEY,WEAVE_ENTITY, andWEAVE_PROJECT_NAMEare set correctly. - Confirm your environment can reach
https://trace.wandb.aiand that the exporter is configured as shown above. - For additional troubleshooting and sampling guidance, see Koog’s OpenTelemetry support.